Charting the Crisis: A Visual Guide to Endangered Species
Related Articles: Charting the Crisis: A Visual Guide to Endangered Species
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Crisis: A Visual Guide to Endangered Species. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Crisis: A Visual Guide to Endangered Species
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16218434/Screen_Shot_2019_05_07_at_9.39.50_AM.png)
The Earth’s biodiversity is facing an unprecedented crisis. Species are disappearing at an alarming rate, driven by human activities that disrupt natural habitats, introduce invasive species, and alter climate patterns. To effectively address this global challenge, a clear understanding of the distribution and threats faced by endangered species is paramount. This is where maps of endangered species play a crucial role, serving as powerful tools for conservation efforts.
Understanding the Importance of Maps of Endangered Species
Maps of endangered species provide a visual representation of the geographical distribution of threatened wildlife and plant life. They serve as a vital resource for scientists, conservationists, and policymakers, enabling them to:
- Identify hotspots of biodiversity: Maps highlight regions with a high concentration of endangered species, allowing conservationists to focus their efforts on areas with the greatest need.
- Track population trends: By mapping the distribution of endangered species over time, researchers can monitor population changes, identify areas experiencing decline, and assess the effectiveness of conservation interventions.
- Prioritize conservation actions: Maps can help prioritize conservation efforts by identifying areas where habitat protection, species reintroduction, or other interventions are most critical.
- Raise public awareness: Visual representations of endangered species and their geographical distribution can effectively engage the public, fostering greater understanding and support for conservation initiatives.
- Inform policy decisions: Maps provide policymakers with essential data to develop effective regulations, allocate resources, and implement conservation strategies.
Types of Maps Used for Endangered Species
Several types of maps are employed to visualize the distribution and threats faced by endangered species:
- Distribution maps: These maps depict the geographical range of a particular species, highlighting areas where it is known to occur.
- Habitat maps: These maps focus on the specific habitats occupied by endangered species, including forests, wetlands, coral reefs, and grasslands.
- Threat maps: These maps identify the major threats facing endangered species, such as habitat loss, poaching, pollution, and climate change.
- Conservation priority maps: These maps combine information on species distribution, threats, and conservation value to prioritize areas for conservation action.
Data Sources and Mapping Techniques
Data for endangered species maps is derived from various sources, including:
- Field surveys: Scientists conduct field surveys to collect data on species presence, abundance, and habitat use.
- Citizen science: Public participation through citizen science projects can contribute valuable data on species sightings and distribution.
- Satellite imagery: Remote sensing techniques using satellite imagery can provide information on habitat characteristics and land-use changes.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software is used to analyze, visualize, and integrate data from various sources to create maps of endangered species.
Benefits of Using Maps in Conservation
Maps of endangered species offer numerous benefits for conservation efforts:
- Improved targeting of conservation efforts: By identifying areas with high concentrations of endangered species, maps allow for efficient allocation of resources and targeted interventions.
- Enhanced understanding of threats: Threat maps provide insights into the factors driving species decline, enabling conservationists to develop effective mitigation strategies.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of conservation actions: Maps can be used to monitor the impact of conservation interventions, allowing for adjustments and improvements in strategies.
- Facilitation of collaboration: Maps provide a common platform for scientists, conservationists, and policymakers to share data and coordinate efforts.
- Increased public awareness: Visual representations of endangered species and their distribution can effectively communicate the urgency of conservation efforts and engage the public in supporting these initiatives.
FAQs about Maps of Endangered Species
1. What is the difference between a distribution map and a habitat map?
A distribution map shows the geographical range of a species, while a habitat map focuses on the specific types of habitats occupied by that species. For example, a distribution map of the African elephant might show its range across sub-Saharan Africa, while a habitat map would depict the specific types of forests, grasslands, and wetlands where elephants are found.
2. How are threat maps used in conservation?
Threat maps identify the major factors driving species decline, such as habitat loss, poaching, pollution, and climate change. This information allows conservationists to prioritize mitigation efforts and develop strategies to address the most pressing threats. For instance, a threat map might highlight areas where deforestation is driving the decline of a particular species, prompting interventions to protect remaining forests.
3. How can maps of endangered species be used to raise public awareness?
Visual representations of endangered species and their distribution can effectively communicate the urgency of conservation efforts. Maps can be used in educational materials, websites, documentaries, and exhibitions to engage the public and foster greater understanding and support for conservation initiatives.
4. What are some examples of successful conservation efforts that have been aided by maps of endangered species?
Maps have played a crucial role in numerous successful conservation efforts, including:
- The recovery of the California condor: Maps helped identify critical nesting areas and facilitate the reintroduction of this critically endangered species.
- The protection of the Amazon rainforest: Maps have been instrumental in identifying areas with high biodiversity and prioritizing conservation efforts in this vital ecosystem.
- The conservation of the Javan rhinoceros: Maps have helped track the population of this critically endangered species and guide conservation efforts to protect remaining individuals.
Tips for Using Maps of Endangered Species Effectively
- Consider the target audience: Tailor the map’s design and content to the intended audience, whether it’s scientists, policymakers, or the general public.
- Use clear and concise labeling: Ensure that all map elements, such as species names, threats, and conservation areas, are clearly labeled and easy to understand.
- Choose appropriate map projections: Select a map projection that accurately represents the geographical distribution of endangered species and avoids distortions.
- Integrate data from multiple sources: Combine data from field surveys, citizen science projects, satellite imagery, and other sources to create comprehensive and informative maps.
- Use interactive maps: Consider using interactive maps that allow users to zoom in, pan, and explore different layers of information.
Conclusion
Maps of endangered species are essential tools for understanding and addressing the global biodiversity crisis. They provide a visual representation of the distribution, threats, and conservation priorities for threatened wildlife and plant life. By using maps effectively, scientists, conservationists, and policymakers can prioritize conservation efforts, monitor progress, and raise public awareness of the urgent need to protect endangered species. As we strive to conserve Earth’s biodiversity for future generations, maps will continue to play a vital role in guiding our efforts to ensure the survival of all species.

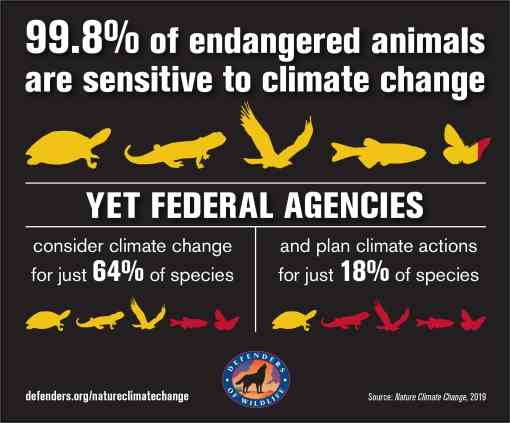
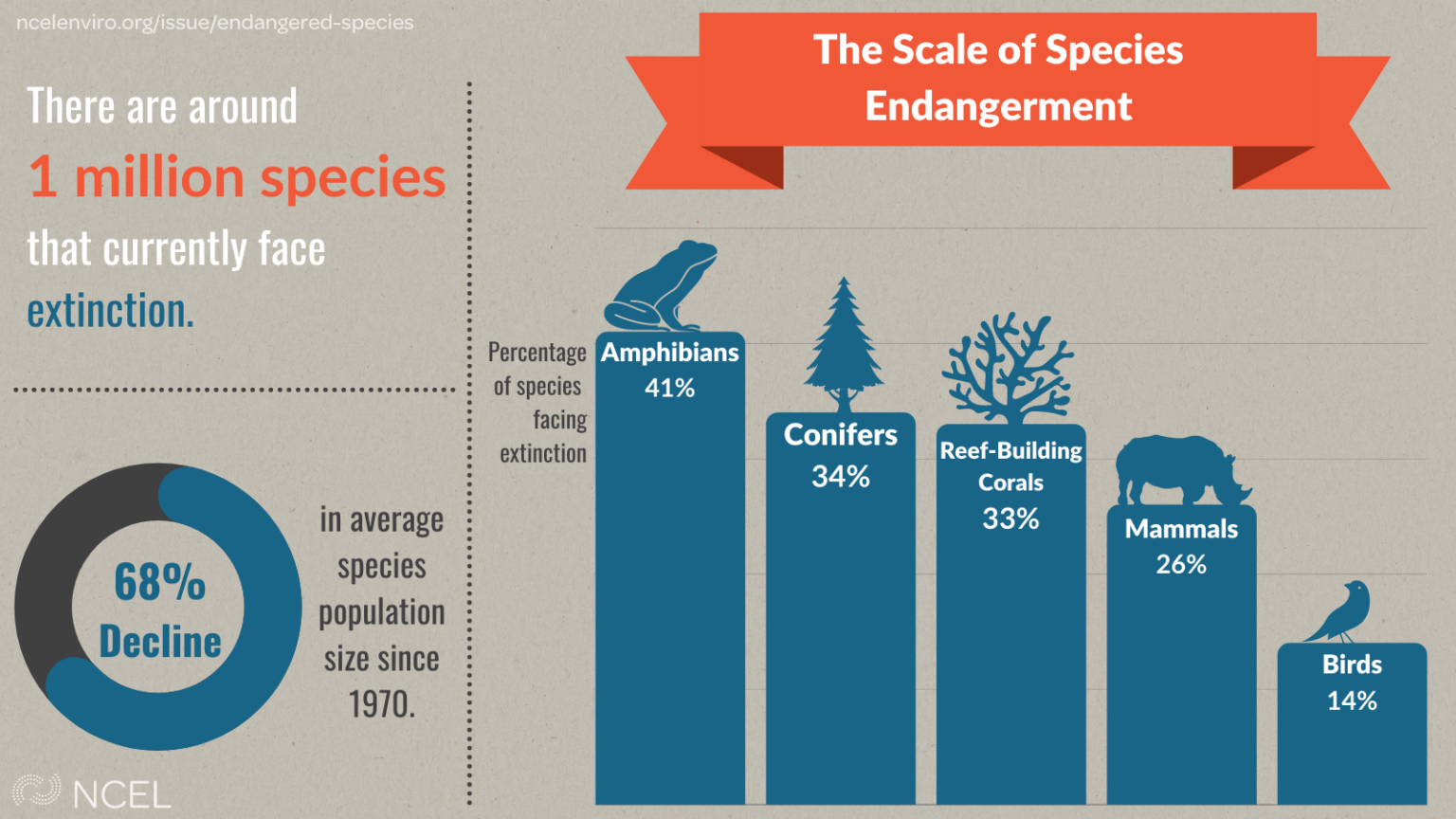



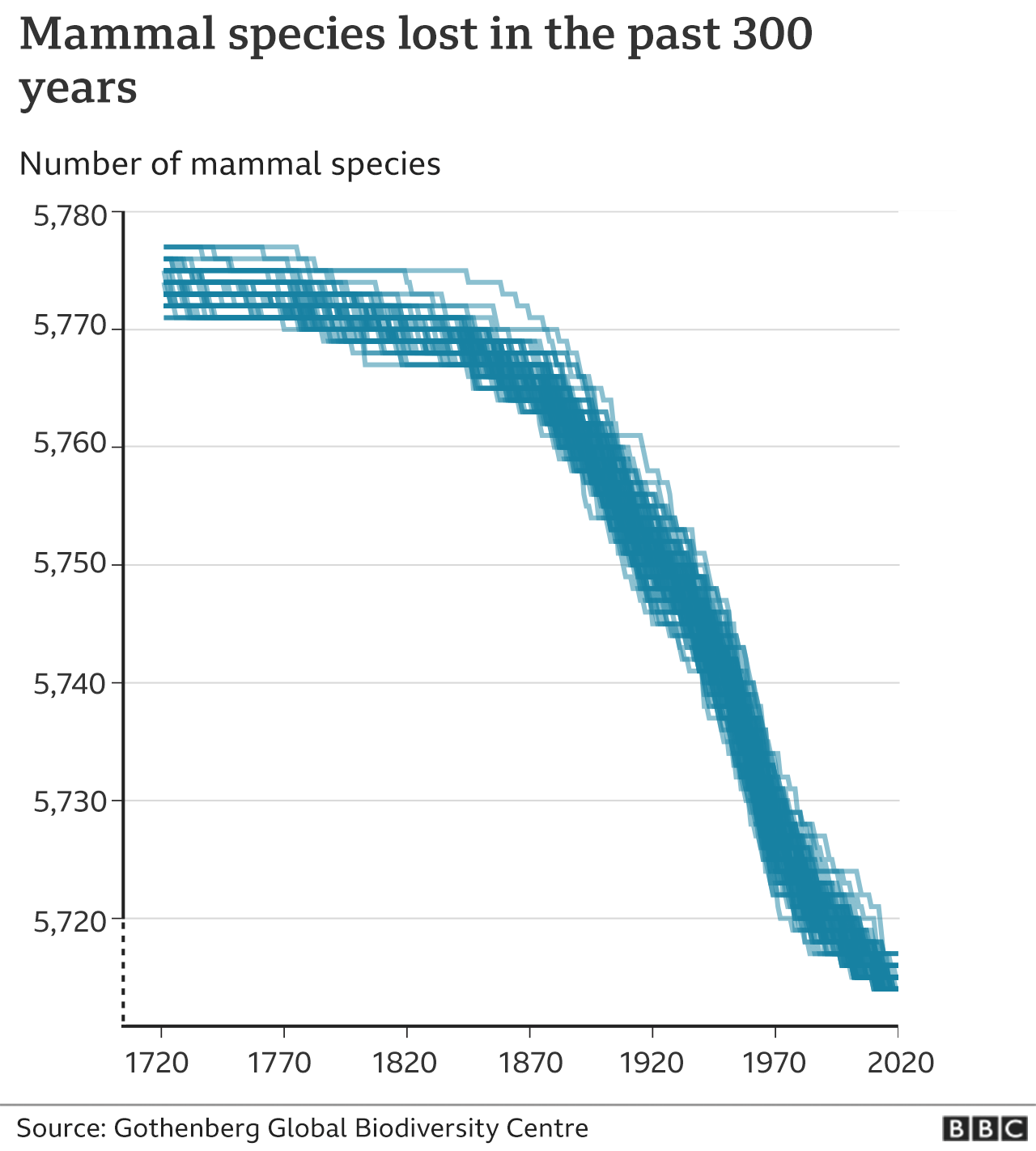
.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Crisis: A Visual Guide to Endangered Species. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!