Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Symbols and Their Crucial Role
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Symbols and Their Crucial Role
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Symbols and Their Crucial Role. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Symbols and Their Crucial Role
Maps, those intricate visual representations of our world, are more than just static images. They are powerful tools of communication, conveying complex information through a carefully constructed system of symbols. These symbols, ranging from simple icons to intricate diagrams, serve as a visual language, enabling us to navigate, understand geographical features, and interpret data about our surroundings.
The Essence of Map Symbols
Map symbols are visual representations that convey specific information about geographical features, locations, or data. Their primary function is to simplify complex information, transforming it into a readily understandable format. This simplification is crucial for map users, as it allows for quick and efficient comprehension of the depicted information.
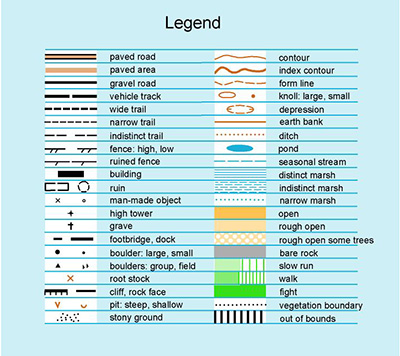
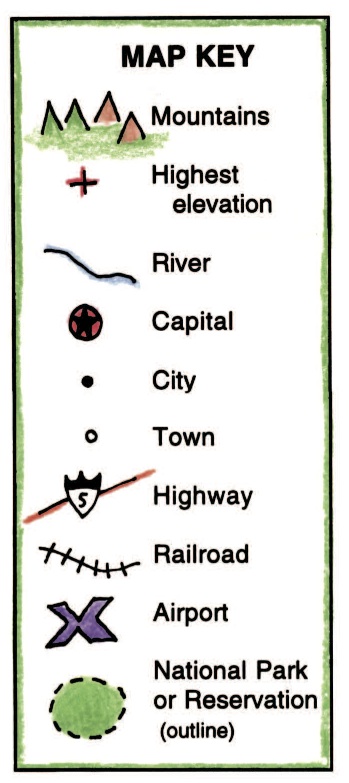
Types of Map Symbols
Map symbols are diverse, reflecting the wide range of information they convey. Broadly categorized, they fall into several key types:
-
Point Symbols: These symbols represent specific locations, such as cities, landmarks, or points of interest. Examples include circles, squares, stars, or unique icons representing specific features like airports, hospitals, or historical sites.
-
Line Symbols: These symbols depict linear features, such as roads, rivers, boundaries, or power lines. They are often represented by lines of varying thickness, color, or pattern, indicating different types of features or their relative importance.
-
Area Symbols: These symbols represent areas or regions, such as forests, lakes, or political boundaries. They are typically depicted by distinct colors, patterns, or textures, allowing for easy differentiation between various land cover types or administrative divisions.
-
Text Symbols: These symbols consist of letters, numbers, or words, providing additional information about the depicted features. Examples include place names, elevation figures, population data, or descriptive labels for specific areas.
Importance of Map Symbols
The significance of map symbols extends beyond their role in conveying information. They contribute to several key aspects of map use:
-
Clarity and Conciseness: Map symbols allow for the efficient presentation of complex data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format. This clarity is crucial for users who need to quickly grasp the information presented on the map.
-
Standardization and Consistency: The use of standardized map symbols ensures consistency across different maps, promoting understanding and reducing ambiguity. This standardization facilitates communication and allows users to readily interpret information across various sources.
-
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Map symbols can be designed to be accessible to users with diverse abilities, including visual impairments. By using a combination of visual and tactile elements, maps can be made more inclusive, allowing wider access to geographical information.
-
Analytical Capabilities: Map symbols, combined with other data layers, enable users to perform spatial analysis, identifying patterns, relationships, and trends in geographical data. This capability is crucial for planning, decision-making, and understanding complex environmental or social issues.
Benefits of Using Map Symbols
The use of map symbols offers several advantages for both map creators and users:
-
Improved Communication: Map symbols facilitate clear and concise communication of geographical information, bridging the gap between complex data and user comprehension.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: By simplifying information, map symbols enable users to quickly and efficiently access and interpret data, leading to faster decision-making and improved task completion.
-
Increased Accessibility: The use of standardized symbols ensures that maps are accessible to a wider audience, promoting understanding and engagement with geographical information.
-
Facilitating Analysis: Map symbols, when combined with other data layers, enable users to perform spatial analysis, unlocking valuable insights and supporting informed decision-making.
FAQs on Map Symbols
1. What are the most common map symbols?
Common map symbols include:
- Point Symbols: Circles, squares, triangles, stars, icons representing specific features (e.g., airport, hospital, school).
- Line Symbols: Solid lines, dashed lines, dotted lines, varying line thicknesses, colored lines representing different road types or boundaries.
- Area Symbols: Different colors, patterns, textures representing land cover types (e.g., forest, water, urban areas), or administrative divisions.
- Text Symbols: Place names, elevation figures, population data, descriptive labels for specific areas.
2. How are map symbols standardized?
Standardization of map symbols is achieved through established guidelines and conventions, such as those provided by the American Cartographic Association (ACA) or the International Cartographic Association (ICA). These guidelines define standard symbols for specific features, ensuring consistency and clarity across different maps.
3. Why are map symbols important for navigation?
Map symbols are crucial for navigation as they provide clear visual cues that guide users to their destination. They indicate landmarks, roads, and other important features, enabling users to efficiently plan their route and navigate unfamiliar areas.
4. How can map symbols be used for environmental analysis?
Map symbols, when combined with data layers representing environmental factors such as vegetation, water bodies, or pollution levels, can be used to analyze environmental trends, identify areas of concern, and support decision-making related to environmental management.
5. How can map symbols be made more accessible?
Map symbols can be made more accessible by using:
- High-contrast colors and patterns: Ensuring that symbols are easily distinguishable by users with visual impairments.
- Tactile symbols: Incorporating embossed or raised symbols that can be felt by users who are blind or visually impaired.
- Audio descriptions: Providing audio descriptions of symbols for users who are blind or visually impaired.
Tips for Using Map Symbols Effectively
- Choose appropriate symbols: Select symbols that are clear, concise, and relevant to the information being conveyed.
- Use standardized symbols: Utilize established symbols whenever possible to ensure consistency and avoid ambiguity.
- Maintain symbol size and spacing: Ensure that symbols are large enough to be easily seen and that sufficient spacing is provided between them to avoid clutter.
- Use color effectively: Select colors that are visually appealing and clearly differentiate between different features.
- Provide a legend: Include a legend that explains the meaning of each symbol used on the map.
Conclusion
Map symbols serve as a vital component of cartographic communication, transforming complex information into easily understandable and accessible visuals. By utilizing a standardized system of symbols, map creators can effectively convey geographical information, facilitating navigation, analysis, and informed decision-making. As technology advances, the use of map symbols continues to evolve, incorporating new forms of representation and incorporating accessibility features to ensure that geographical information remains accessible to all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Symbols and Their Crucial Role. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!