Navigating the Flow of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Flow of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Flow of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Flow of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps

The world’s energy infrastructure is a complex and intricate web, with pipelines serving as critical arteries for the transportation of essential resources. These pipelines, often stretching across vast distances, facilitate the movement of oil, natural gas, and other energy commodities from production sites to consumption centers, driving economies and fueling industries. Understanding the intricate network of these pipelines, their routes, and their capacities is essential for various stakeholders, including energy companies, policymakers, and the public. This is where energy transfer pipeline maps come into play.
Understanding Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
An energy transfer pipeline map is a visual representation of the pipeline network that transports energy resources. These maps offer a comprehensive overview of the pipeline infrastructure, providing insights into key aspects such as:
- Pipeline Routes: The maps clearly depict the geographical paths of pipelines, showcasing the locations of origin, destination, and intermediate points.
- Pipeline Types: Different pipeline types, such as crude oil pipelines, natural gas pipelines, and refined product pipelines, are often differentiated on the maps, offering clarity about the specific resources being transported.
- Pipeline Capacities: The maps may indicate the carrying capacity of each pipeline, providing information about the volume of energy resources that can be transported.
- Pipeline Operators: The maps can identify the companies responsible for operating and maintaining each pipeline segment, offering insights into the ownership and control of the energy infrastructure.
- Major Hubs and Terminals: Key locations, such as production sites, processing facilities, and storage terminals, are often marked on the maps, highlighting the crucial points within the energy supply chain.
The Importance of Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
Energy transfer pipeline maps hold immense value for a wide range of stakeholders, providing crucial information that supports informed decision-making and efficient operations:
- Energy Companies: Pipeline maps are essential tools for energy companies, enabling them to optimize resource allocation, plan pipeline expansions, and assess potential risks.
- Policymakers: Governments and regulatory bodies rely on these maps to understand the energy infrastructure landscape, formulate policies, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of pipelines.
- Financial Institutions: Investors and lenders utilize pipeline maps to assess the financial viability of energy projects and evaluate the risks associated with pipeline infrastructure.
- Environmental Organizations: Environmental groups use pipeline maps to identify potential environmental impacts and advocate for responsible pipeline construction and operation.
- The Public: These maps provide the public with a visual understanding of the energy infrastructure that powers their lives, fostering awareness and promoting transparency.
Types of Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
Energy transfer pipeline maps come in various forms, each offering a specific level of detail and serving different purposes:
- General Overview Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of the pipeline network, highlighting major routes and key locations, often used for educational purposes or public awareness.
- Detailed Regional Maps: These maps focus on specific geographical areas, offering more granular information about pipeline routes, capacities, and operators within a particular region.
- Interactive Online Maps: These maps allow users to explore pipeline data dynamically, enabling them to zoom in on specific areas, access detailed information about individual pipelines, and even track the movement of energy resources in real time.
- 3D Pipeline Maps: These maps provide a three-dimensional representation of the pipeline network, offering a more realistic and immersive visualization of the infrastructure.
Benefits of Utilizing Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
The use of energy transfer pipeline maps offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Transparency: Maps promote transparency in the energy sector, providing stakeholders with a clear understanding of the pipeline infrastructure and its operations.
- Improved Decision-Making: Maps equip stakeholders with the necessary information to make informed decisions about energy production, transportation, and consumption.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Maps facilitate the identification and assessment of potential risks associated with pipeline operations, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
- Improved Efficiency: Maps enable the optimization of pipeline operations, maximizing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Increased Public Awareness: Maps contribute to public awareness about the importance of energy infrastructure and the role of pipelines in supporting modern society.
FAQs Regarding Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps
Q: Where can I find reliable energy transfer pipeline maps?
A: Reliable energy transfer pipeline maps can be found through various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: National and regional energy regulatory agencies often publish pipeline maps on their websites.
- Industry Associations: Associations representing energy companies and pipeline operators may provide access to pipeline maps.
- Energy Data Providers: Specialized data providers offer comprehensive pipeline maps and related information.
- Academic Institutions: Research institutions and universities may conduct research on pipeline infrastructure and publish maps as part of their findings.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when evaluating energy transfer pipeline maps?
A: When evaluating energy transfer pipeline maps, it is crucial to consider:
- Accuracy and Reliability: Ensure that the map data is accurate, up-to-date, and sourced from reliable sources.
- Level of Detail: Choose a map that provides the appropriate level of detail for your specific needs.
- Ease of Use: Select a map that is easy to navigate and interpret, with clear labels and intuitive features.
- Data Accessibility: Ensure that the map provides access to relevant data, such as pipeline capacities, operators, and environmental impact information.
Q: How are energy transfer pipeline maps used in environmental assessments?
A: Energy transfer pipeline maps play a crucial role in environmental assessments by:
- Identifying Potential Impacts: Maps help identify potential environmental impacts of pipeline construction and operation, such as habitat fragmentation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Planning Mitigation Measures: Maps assist in planning and implementing mitigation measures to minimize environmental damage, such as avoiding sensitive areas and using environmentally friendly construction techniques.
- Monitoring Environmental Performance: Maps can be used to monitor the environmental performance of pipelines over time, ensuring compliance with regulations and identifying any potential issues.
Tips for Using Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps Effectively
- Understand the Map’s Scope: Before using a pipeline map, clearly define the geographical area and specific information you need.
- Pay Attention to Data Sources: Verify the data sources used to create the map, ensuring their reliability and accuracy.
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: Choose a map that aligns with your specific needs, whether it’s for educational purposes, policy analysis, or business decision-making.
- Utilize Additional Resources: Combine pipeline maps with other relevant data sources, such as environmental impact reports, regulatory documents, and energy market analyses.
Conclusion
Energy transfer pipeline maps are indispensable tools for navigating the complex world of energy infrastructure. They provide a visual representation of the pipeline network, offering critical insights into pipeline routes, capacities, operators, and key locations. By understanding the information conveyed by these maps, stakeholders can make informed decisions, optimize operations, mitigate risks, and contribute to the responsible and sustainable development of the energy sector. As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, energy transfer pipeline maps will remain essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable flow of energy resources to meet the demands of a growing population.
![US Pipeline Map Printable [Pipeline Map of US]](https://unitedstatesmaps.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/us-pipeline-map.jpg)
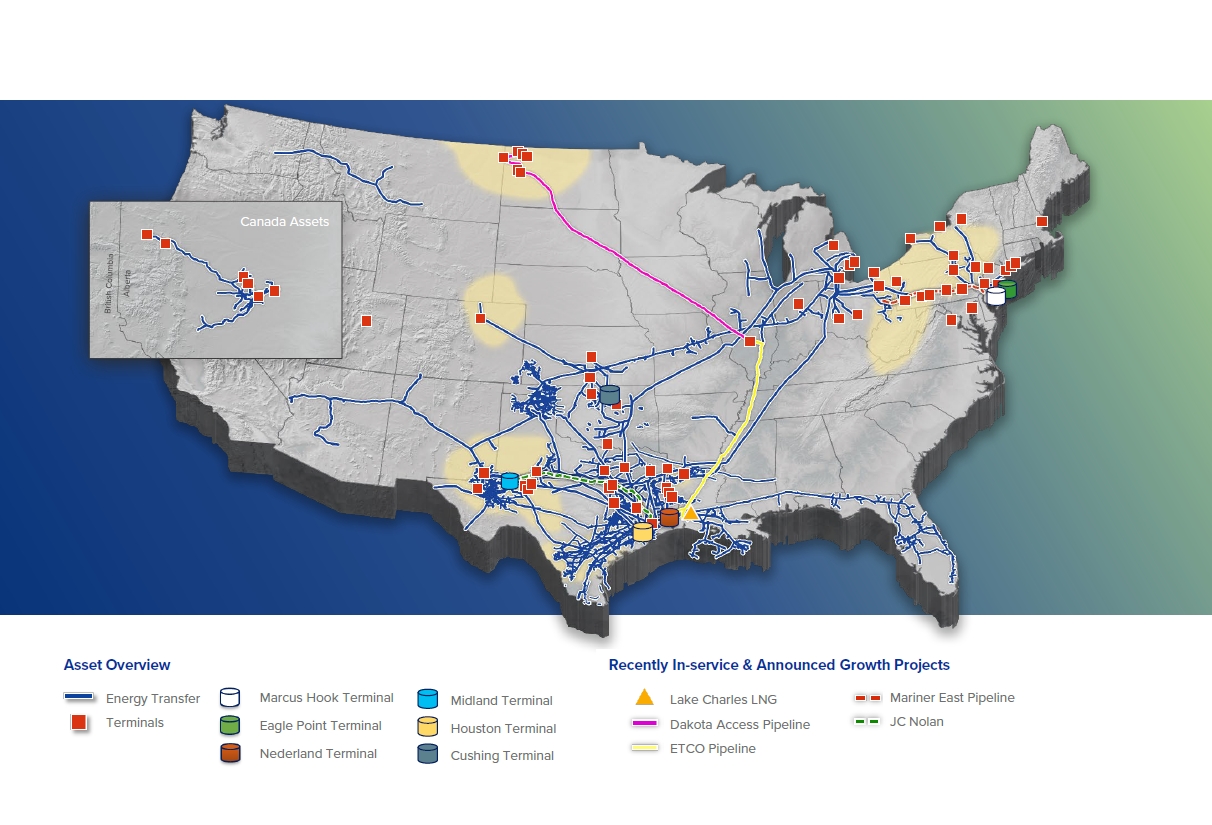
![US Pipeline Map Printable [Pipeline Map of US]](https://unitedstatesmaps.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/pipeline-map-of-us.jpg)



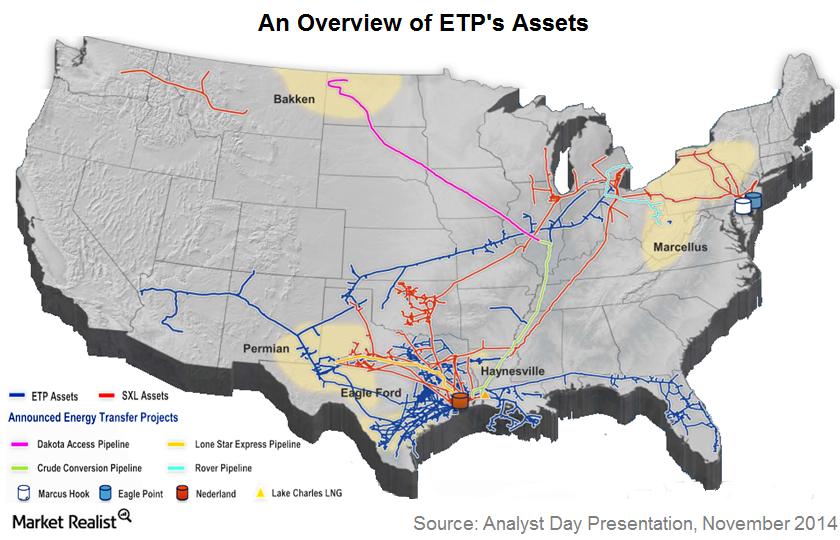

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Flow of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Energy Transfer Pipeline Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!