Navigating the Landscape of Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Health Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Health Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Health Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Health Maps
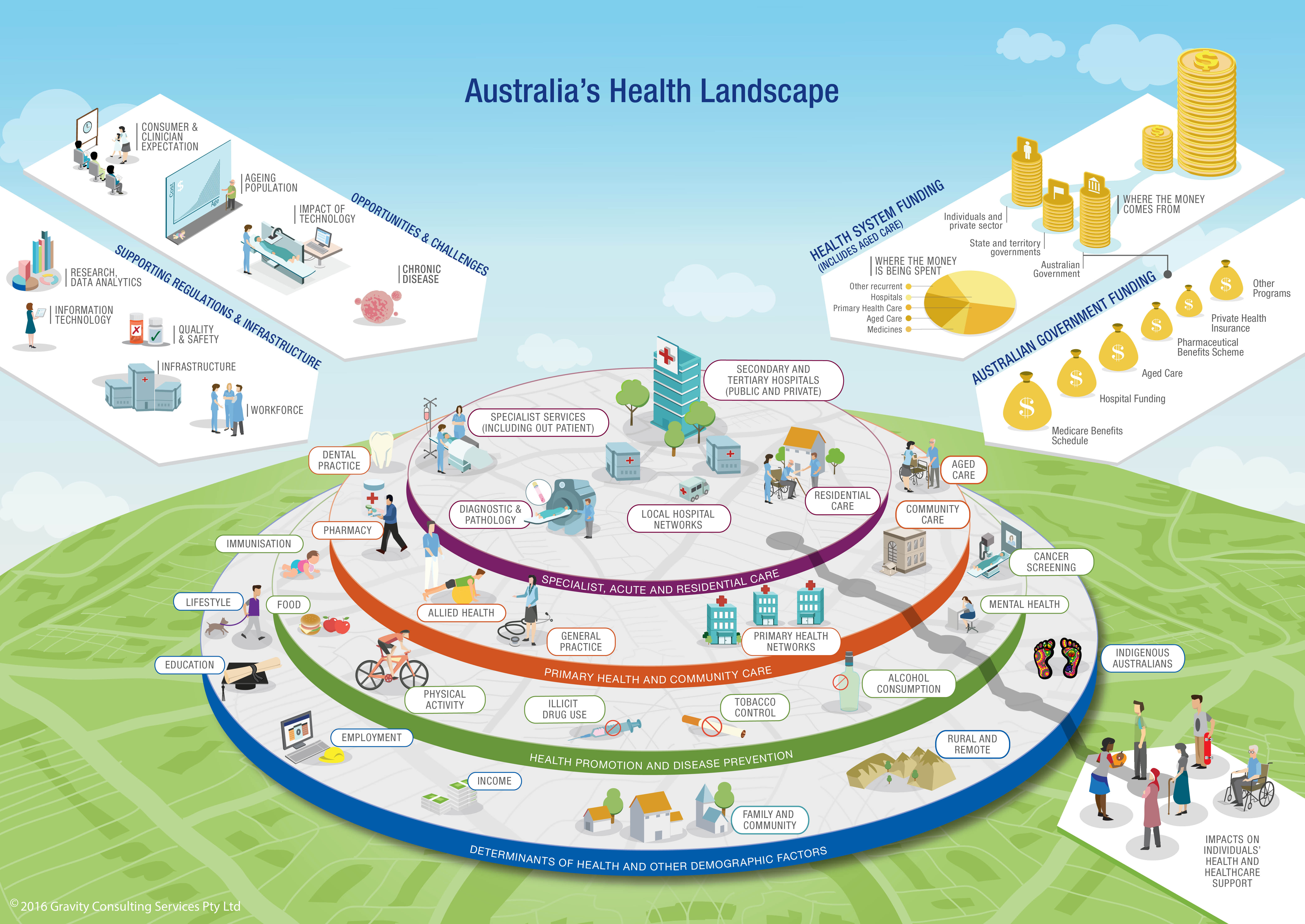
The intricate web of healthcare systems and services can be challenging to navigate, even for seasoned professionals. A central health map, however, provides a powerful tool for understanding and managing the complexities of this landscape. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of central health maps, exploring their components, benefits, and applications in various healthcare settings.
Understanding the Core: What is a Central Health Map?
A central health map serves as a visual representation of a healthcare system’s infrastructure, encompassing its diverse components and their interconnectedness. It goes beyond a simple list of hospitals and clinics, offering a detailed snapshot of the healthcare ecosystem within a specific region or organization.
Key Elements of a Central Health Map:
- Healthcare Providers: This includes hospitals, clinics, physician practices, specialized care centers, and other healthcare facilities. The map details their geographic locations, service offerings, and capacity.
- Patient Population: The map considers the demographic characteristics of the patient population served, including age, gender, socioeconomic status, and health needs.
- Health Services: This encompasses the range of medical services offered, from primary care to specialized treatments, encompassing preventative services, diagnostics, and rehabilitation.
- Information Flow: The map highlights the communication channels and data exchange systems within the healthcare system, including electronic health records, patient portals, and referral networks.
- Infrastructure: This element includes the physical infrastructure of healthcare facilities, transportation networks, and communication systems.
- Resource Allocation: The map provides insights into the distribution of healthcare resources, including staffing levels, equipment availability, and financial resources.
Benefits of Central Health Maps:
The application of central health maps extends far beyond mere visualization. They offer tangible benefits across various healthcare settings, contributing to improved efficiency, effectiveness, and patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Coordination and Collaboration: Central health maps foster seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, facilitating efficient patient referrals, shared information, and coordinated care plans.
- Resource Optimization: By providing a clear picture of resource availability, central health maps enable healthcare organizations to allocate resources effectively, ensuring optimal utilization and minimizing waste.
- Improved Patient Access: Central health maps can be used to identify areas with limited healthcare access and guide the development of strategies to expand services and reach underserved populations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Central health maps provide valuable data insights, enabling informed decision-making regarding resource allocation, service expansion, and strategic planning.
- Effective Disaster Planning: In emergency situations, central health maps can facilitate rapid response by providing a clear understanding of available resources, patient populations, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Quality Improvement: By highlighting potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement, central health maps facilitate the development and implementation of quality improvement initiatives.
Applications of Central Health Maps:
Central health maps find diverse applications across various healthcare settings, serving as essential tools for:
- Healthcare Organizations: Hospitals, clinics, and integrated health systems leverage central health maps to optimize resource allocation, improve patient flow, and enhance coordination of care.
- Government Agencies: Public health agencies utilize central health maps for population health surveillance, resource allocation, and planning for public health emergencies.
- Insurance Companies: Health insurers use central health maps to understand provider networks, assess cost trends, and develop strategies for managing healthcare costs.
- Research Institutions: Researchers utilize central health maps to identify trends in healthcare utilization, analyze health disparities, and conduct epidemiological studies.
FAQs Regarding Central Health Maps:
1. What are the challenges associated with developing and maintaining a central health map?
Developing and maintaining a central health map requires significant data collection, integration, and ongoing updates. Challenges include data privacy concerns, ensuring data accuracy, and maintaining system security.
2. How can technology enhance the effectiveness of central health maps?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology plays a pivotal role in creating interactive and dynamic central health maps. Data visualization tools, real-time data updates, and integration with electronic health records enhance the utility of these maps.
3. What are the future directions for central health maps?
Future advancements in central health maps are likely to focus on incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics, personalized health recommendations, and automated resource allocation.
Tips for Implementing a Central Health Map:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and intended outcomes of implementing a central health map.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders, including healthcare providers, administrators, and patients, throughout the development process.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data used to create the map.
- Utilize User-Friendly Interfaces: Develop an intuitive and user-friendly interface for accessing and interpreting the map.
- Embrace Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update the map based on feedback and changing healthcare needs.
Conclusion:
Central health maps provide a valuable tool for navigating the complex landscape of healthcare systems. By offering a comprehensive visual representation of healthcare infrastructure, resources, and patient populations, these maps empower healthcare organizations, government agencies, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions, improve coordination of care, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, central health maps will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of healthcare.




![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Health Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!