Navigating the World: A Guide to AP World History Map Regions
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Guide to AP World History Map Regions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Guide to AP World History Map Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Guide to AP World History Map Regions
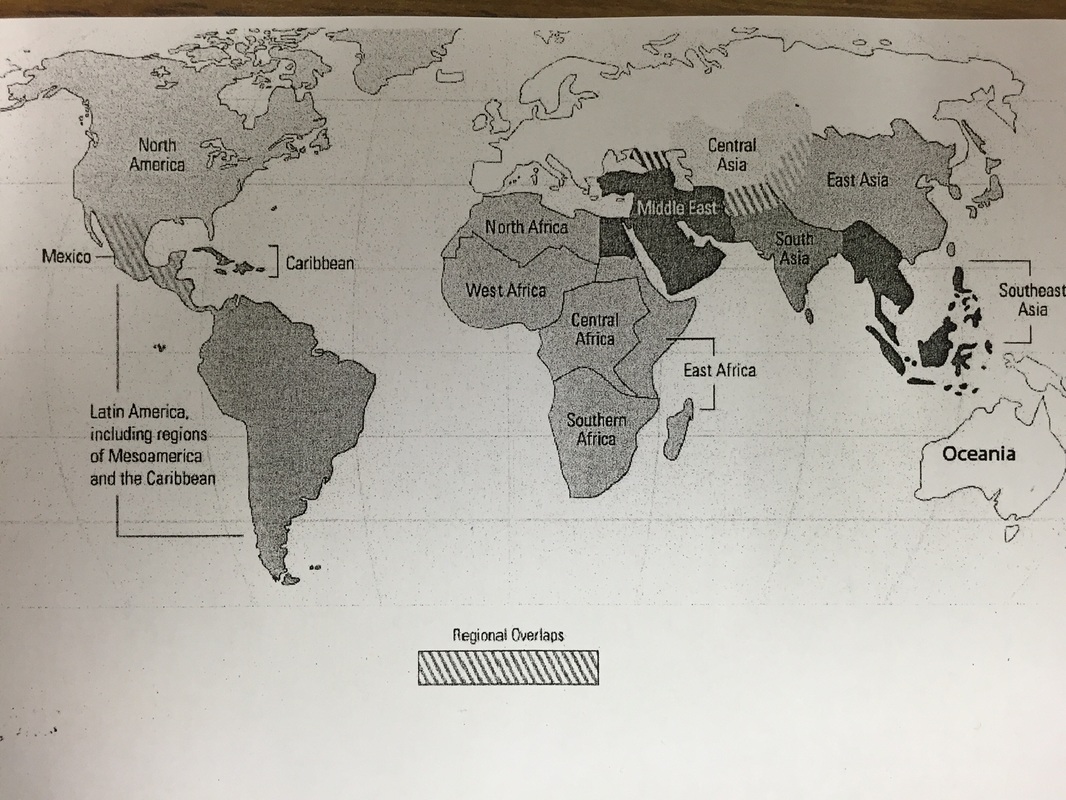
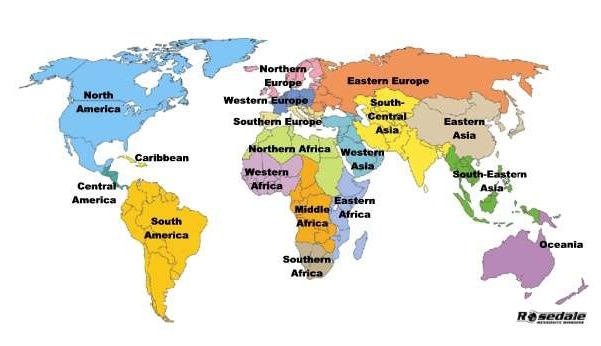
The study of world history is an expansive journey, encompassing the interconnected narratives of diverse cultures, civilizations, and societies across time and space. To effectively navigate this vast landscape, AP World History utilizes a regional framework, dividing the world into six distinct regions. These regions, each with its unique historical trajectory, serve as crucial lenses through which students can analyze and understand the complexities of global history.
1. The Americas:
Spanning from the frozen north to the tip of South America, the Americas encompass a rich tapestry of cultures, from the intricate civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca to the diverse indigenous communities that thrived in the region. This region’s history is marked by the arrival of European powers, the subsequent colonization and exploitation, and the eventual struggles for independence.
Key Themes and Events:
- Pre-Columbian Civilizations: The development of complex societies like the Maya, Aztec, and Inca, characterized by sophisticated urban centers, advanced agriculture, and intricate social structures.
- European Colonization: The arrival of European powers, the establishment of colonial empires, and the devastating impact on indigenous populations through disease, forced labor, and cultural disruption.
- Independence Movements: The struggles for independence from European control, leading to the formation of new nations and the ongoing challenges of nation-building.
- Economic and Social Change: The impact of globalization, industrialization, and modernization on the Americas, with varying degrees of success and challenges.
2. East Asia:
East Asia encompasses a diverse array of civilizations, including China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, each with its unique cultural and historical traditions. This region has been a center of innovation and cultural exchange, witnessing the rise and fall of dynasties, the development of advanced technologies, and the influence of Confucianism and other philosophies.
Key Themes and Events:
- Dynastic Cycles: The cyclical rise and fall of dynasties in China, with each period marked by political, economic, and social changes.
- Cultural Exchange and Diffusion: The spread of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices between China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, shaping the region’s development.
- Imperialism and Modernization: The impact of European colonialism, the rise of Japan as a regional power, and the complex process of modernization in the region.
- Post-World War II Developments: The division of Korea, the rise of China as a global power, and the ongoing challenges of economic development and political stability.
3. South and Southeast Asia:
This region encompasses a diverse array of cultures and civilizations, including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and the Southeast Asian nations. South and Southeast Asia have long been crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, marked by the influence of Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and other religions.
Key Themes and Events:
- Ancient Civilizations: The rise and development of ancient civilizations in the Indus Valley, the Ganges River Valley, and Southeast Asia, each with its unique cultural and religious traditions.
- Trade Networks: The development of extensive trade networks connecting South and Southeast Asia to the rest of the world, leading to the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Colonialism and Independence: The impact of European colonialism on the region, the struggles for independence, and the challenges of nation-building in the post-colonial era.
- Economic and Social Change: The rapid economic growth and modernization of some nations, alongside persistent poverty and social inequality in others.
4. Europe:
Europe, the cradle of Western civilization, has played a pivotal role in shaping global history. From the ancient Greeks and Romans to the Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution, Europe has witnessed significant technological advancements, cultural revolutions, and political upheavals.
Key Themes and Events:
- Classical Antiquity: The rise and fall of the Greek and Roman civilizations, laying the foundation for Western culture and political systems.
- Medieval Period: The development of feudalism, the rise of the Catholic Church, and the emergence of nation-states in Europe.
- Renaissance and Reformation: The cultural and intellectual rebirth of Europe, leading to scientific discoveries, artistic innovation, and religious reform.
- Industrial Revolution and Imperialism: The rapid technological advancements and economic growth of Europe, accompanied by the expansion of European empires across the globe.
- Modern Europe: The tumultuous 20th century, marked by World Wars, political revolutions, and the rise of new ideologies.
5. Africa:
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and civilizations. Its history is marked by the rise and fall of empires, the transatlantic slave trade, and the struggle for independence from European colonialism.
Key Themes and Events:
- Ancient Civilizations: The development of ancient civilizations in Egypt, Nubia, and other parts of Africa, characterized by advanced agriculture, political systems, and cultural achievements.
- Transatlantic Slave Trade: The forced migration of millions of Africans to the Americas, resulting in devastating social and economic consequences for both Africa and the Americas.
- Colonialism and Independence: The impact of European colonization on Africa, the struggles for independence, and the ongoing challenges of nation-building.
- Economic and Social Change: The rapid economic growth and modernization of some African nations, alongside persistent poverty, inequality, and conflict in others.
6. The Middle East and North Africa (MENA):
This region encompasses a diverse array of cultures, languages, and civilizations, including the Arab world, Persia, and Turkey. The MENA region has been a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, marked by the influence of Islam, the rise and fall of empires, and the ongoing challenges of political instability and conflict.
Key Themes and Events:
- Ancient Civilizations: The rise and development of ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Persia, laying the foundation for the region’s cultural and political traditions.
- Islam and the Rise of Empires: The emergence of Islam, the spread of Islamic empires across the region, and the development of Islamic culture and learning.
- Ottoman Empire and Modernization: The rise and fall of the Ottoman Empire, the impact of European imperialism, and the challenges of modernization in the region.
- Political and Economic Challenges: The ongoing conflicts, political instability, and economic disparities in the MENA region, alongside the challenges of democracy and human rights.
The Importance of the Regional Framework:
The regional framework used in AP World History provides a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of global history. By focusing on specific regions, students can:
- Gain a Deeper Understanding of Regional Histories: By studying the unique historical trajectories of each region, students can develop a nuanced understanding of the factors that shaped their development.
- Analyze Interconnections and Comparisons: The regional framework allows students to compare and contrast different regions, identifying patterns of interaction, exchange, and conflict across time and space.
- Develop Critical Thinking Skills: By analyzing historical events within a regional context, students can develop their ability to analyze evidence, draw conclusions, and formulate arguments.
- Gain a Global Perspective: By studying multiple regions, students can develop a global perspective, recognizing the interconnectedness of events and understanding the impact of global processes on individual societies.
FAQs about AP World History Map Regions:
Q: Why are these regions important to the study of world history?
A: These regions represent key centers of civilization and cultural exchange, each with its unique historical trajectory. Understanding these regions allows students to grasp the interconnectedness of global history and appreciate the diversity of human experience.
Q: How do these regions interact with each other throughout history?
A: These regions have interacted through trade, migration, conquest, and cultural exchange, shaping the course of global history. For example, the Silk Road connected East Asia to Europe and the Middle East, while the transatlantic slave trade linked Africa to the Americas.
Q: Are there any specific events or themes that connect these regions?
A: Several themes and events connect these regions, such as the impact of colonialism, the rise of globalization, and the challenges of modernization. Examining these themes across different regions helps students understand their global implications.
Q: How can I best utilize the regional framework in my studies?
A: Focus on understanding the key themes and events within each region, compare and contrast different regions, and analyze the interconnectedness of events across time and space. Utilize maps and timelines to visualize the geographical and chronological context of historical events.
Tips for Studying AP World History Map Regions:
- Utilize Maps: Maps are essential tools for understanding the geographical context of historical events. Use maps to visualize the location of key civilizations, trade routes, and empires.
- Create Timelines: Timelines help visualize the chronological sequence of events within each region and across different regions.
- Focus on Key Themes and Events: Identify the key themes and events within each region, paying attention to their significance and impact.
- Compare and Contrast: Analyze the similarities and differences between different regions, highlighting patterns of interaction, exchange, and conflict.
- Engage with Primary Sources: Explore primary sources, such as historical documents, artifacts, and images, to gain a firsthand perspective on the events and experiences of different regions.
- Utilize Online Resources: Online resources, such as websites, videos, and interactive maps, can provide valuable insights and perspectives on the study of world history.
Conclusion:
The regional framework used in AP World History offers a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of global history. By focusing on specific regions, students can gain a deeper understanding of regional histories, analyze interconnections and comparisons, develop critical thinking skills, and gain a global perspective. Through the study of these regions, students can embark on a journey of discovery, exploring the rich tapestry of human history and appreciating the interconnectedness of our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Guide to AP World History Map Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
