The Pacific Ocean and the United States: A Coastal Tapestry
Related Articles: The Pacific Ocean and the United States: A Coastal Tapestry
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Pacific Ocean and the United States: A Coastal Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Pacific Ocean and the United States: A Coastal Tapestry

The Pacific Ocean, the largest and deepest of Earth’s oceanic bodies, plays a pivotal role in shaping the geography, economy, and culture of the United States. Its vast expanse, stretching from the Arctic Circle to the Southern Ocean, forms a critical component of the nation’s western border, influencing everything from climate patterns to maritime trade routes. Understanding the relationship between the Pacific Ocean and the United States requires a deep dive into the intricate tapestry of their intertwined history, geography, and contemporary relevance.
A Coastal Landscape of Diversity
The Pacific coastline of the United States, spanning over 12,000 miles, presents a diverse landscape, ranging from rugged cliffs and sandy beaches to lush rainforests and towering mountains. This coastline is home to a multitude of ecosystems, from the vibrant coral reefs of Hawaii to the temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest. The Pacific Ocean’s influence on these ecosystems is profound, shaping their biodiversity and contributing to their unique character.
The Pacific Ocean’s Influence on Climate
The Pacific Ocean plays a crucial role in regulating the climate of the United States, particularly the western states. The vast expanse of water acts as a giant heat sink, absorbing solar energy and moderating temperatures. This moderating effect results in milder winters and cooler summers along the coast, compared to inland regions. Additionally, the Pacific Ocean is responsible for various weather phenomena, including El Niño and La Niña, which can have significant impacts on precipitation patterns, agricultural yields, and the severity of natural disasters.
The Pacific Ocean as a Lifeline for Trade
The Pacific Ocean has served as a vital trade route for centuries, connecting the United States to Asia, Oceania, and Latin America. The development of modern shipping technology has further enhanced the importance of the Pacific Ocean for international trade, making it a cornerstone of the global economy. The major ports along the Pacific coast, such as Los Angeles, Long Beach, and Seattle, serve as gateways for billions of dollars worth of goods, contributing significantly to the US economy.
A Source of Natural Resources
The Pacific Ocean is a rich source of natural resources, including fish, oil, and gas. The United States has a long history of fishing in the Pacific, with industries ranging from commercial fishing to recreational angling. The ocean also holds significant reserves of oil and gas, although their extraction remains a contentious issue due to environmental concerns.
A Tapestry of Cultural and Historical Significance
The Pacific Ocean has profoundly influenced the history and culture of the United States. From the arrival of European explorers to the rise of the American West, the ocean has played a central role in shaping the nation’s identity. The Pacific Ocean has also served as a bridge for cultural exchange, fostering connections between the United States and other Pacific Rim nations.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the Pacific Ocean offers numerous benefits, it also presents a range of challenges. Climate change is a pressing concern, with rising sea levels threatening coastal communities and impacting marine ecosystems. Pollution from industrial activities and shipping continues to pose a threat to the ocean’s health. Additionally, the increasing demand for natural resources, particularly oil and gas, raises concerns about environmental sustainability.
Navigating the Future
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach, involving governments, industries, and communities. Sustainable practices, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating pollution, and managing fisheries responsibly, are crucial for safeguarding the Pacific Ocean’s health and ensuring its continued economic and cultural importance.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest port in the Pacific Ocean on the US West Coast?
A: The Port of Los Angeles is the largest port in the Pacific Ocean on the US West Coast, handling a significant volume of containerized cargo and contributing significantly to the regional and national economy.
Q: What are the major islands in the Pacific Ocean that belong to the United States?
A: The major islands in the Pacific Ocean that belong to the United States include Hawaii, Guam, American Samoa, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. These islands have distinct cultures and histories, contributing to the diversity of the United States.
Q: How does the Pacific Ocean influence the climate of the United States?
A: The Pacific Ocean plays a crucial role in moderating the climate of the United States, particularly the western states. Its vast expanse acts as a heat sink, absorbing solar energy and moderating temperatures. This results in milder winters and cooler summers along the coast compared to inland regions.
Q: What are the major industries that rely on the Pacific Ocean?
A: The Pacific Ocean supports a wide range of industries, including fishing, shipping, tourism, and energy production. These industries contribute significantly to the US economy and provide employment opportunities for millions of Americans.
Q: What are the environmental challenges facing the Pacific Ocean?
A: The Pacific Ocean faces numerous environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction. These challenges threaten the health of marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of coastal communities.
Tips for Engaging with the Pacific Ocean
1. Support Sustainable Practices: Choose seafood from sustainable sources, reduce plastic consumption, and support organizations working to protect the ocean environment.
2. Learn about the Pacific Ocean’s Ecosystems: Explore local marine reserves, visit aquariums, and educate yourself about the diverse species that inhabit the Pacific Ocean.
3. Engage in Coastal Conservation: Participate in beach cleanups, volunteer with organizations working to protect coastal habitats, and advocate for policies that promote ocean conservation.
4. Support Responsible Tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tour operators, minimize your environmental footprint, and respect the local culture and environment.
Conclusion
The Pacific Ocean is an integral part of the United States, shaping its geography, climate, economy, and culture. Understanding the complex relationship between the ocean and the nation is crucial for addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By fostering sustainable practices, promoting responsible resource management, and engaging in thoughtful stewardship, we can ensure the continued health and vitality of this vital resource for generations to come.
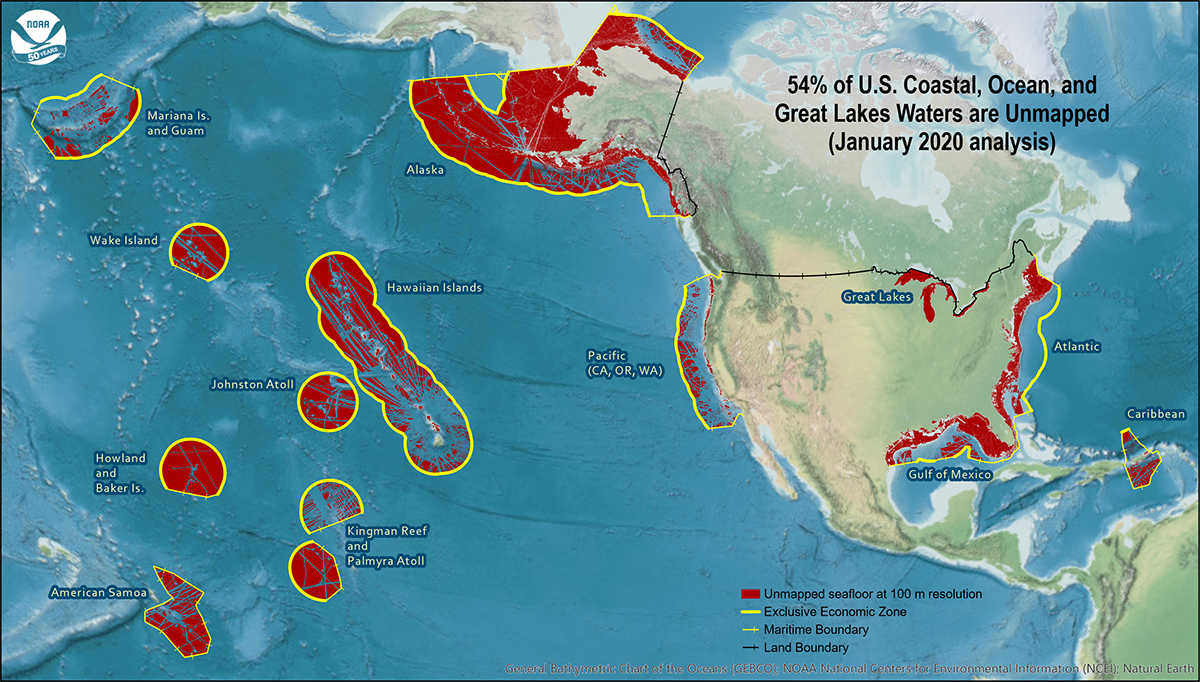
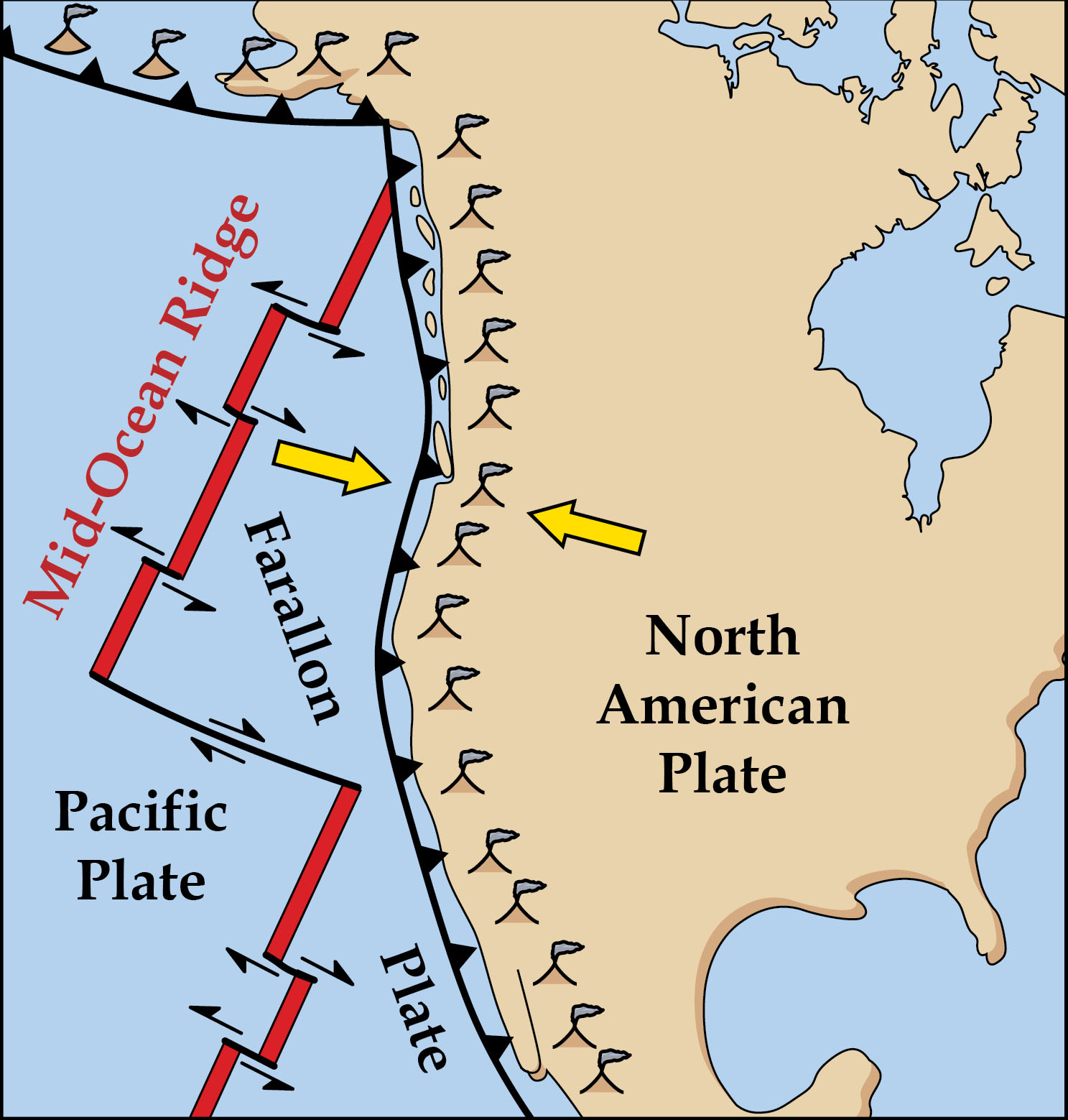


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Pacific Ocean and the United States: A Coastal Tapestry. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!