The Palk Strait: A Bridge Between Nations and a Gateway to History
Related Articles: The Palk Strait: A Bridge Between Nations and a Gateway to History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Palk Strait: A Bridge Between Nations and a Gateway to History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Palk Strait: A Bridge Between Nations and a Gateway to History

The Palk Strait, a narrow stretch of water separating India and Sri Lanka, is more than just a geographical feature. It is a historical crossroads, a bustling maritime route, and a vital ecological zone. This article delves into the intricacies of the Palk Strait, exploring its geographical significance, historical importance, ecological diversity, and the challenges it faces.
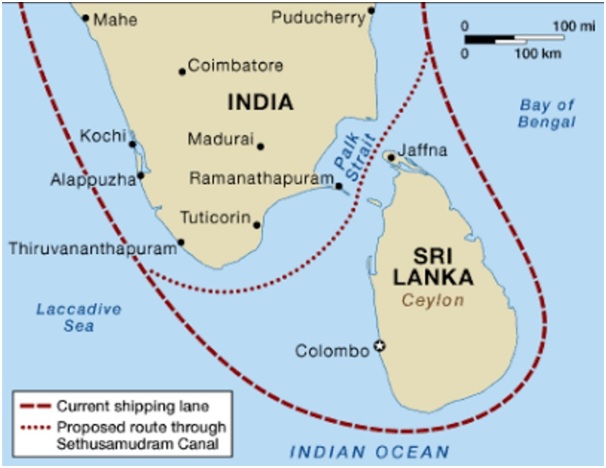
A Geographic Overview
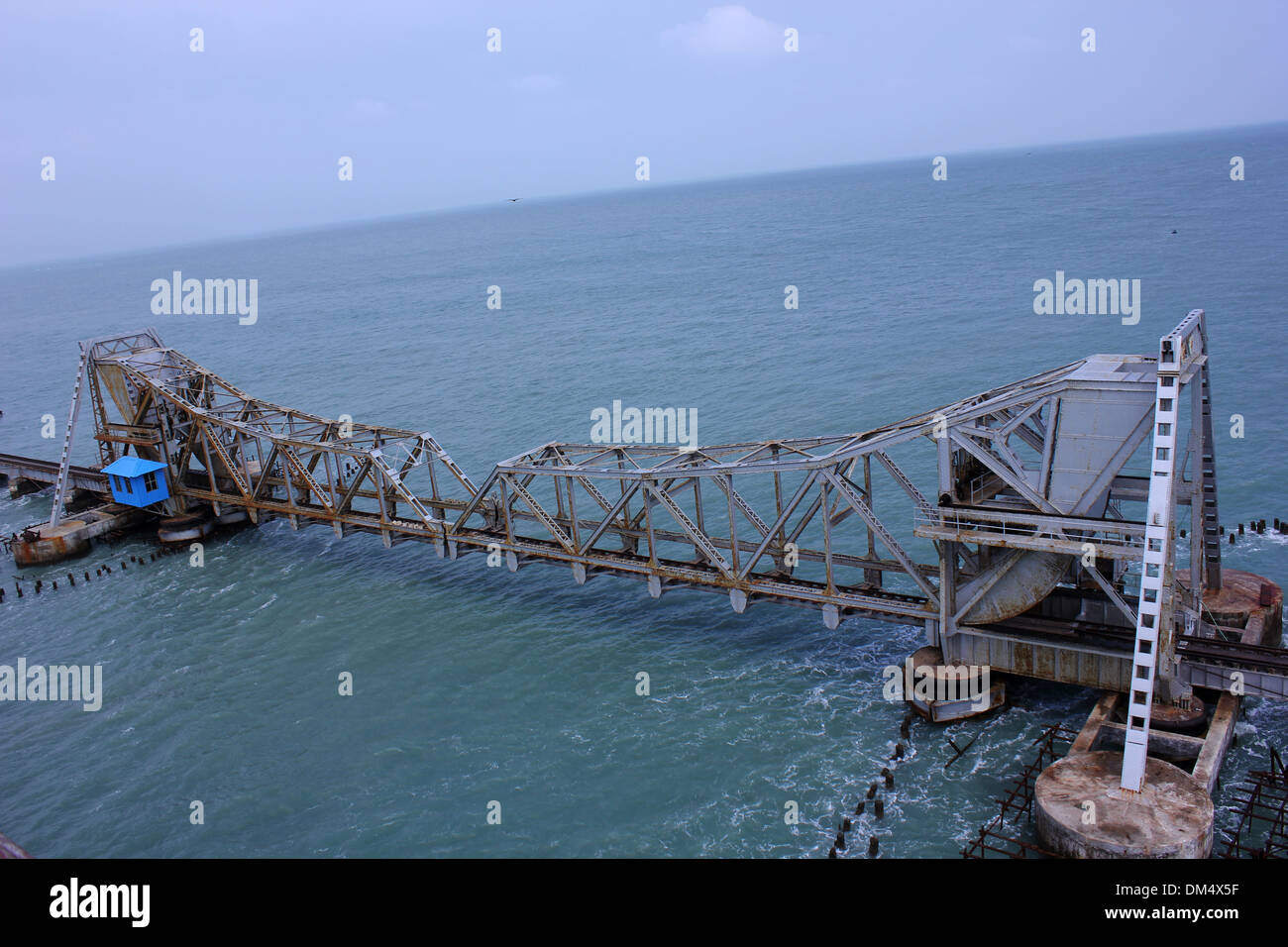
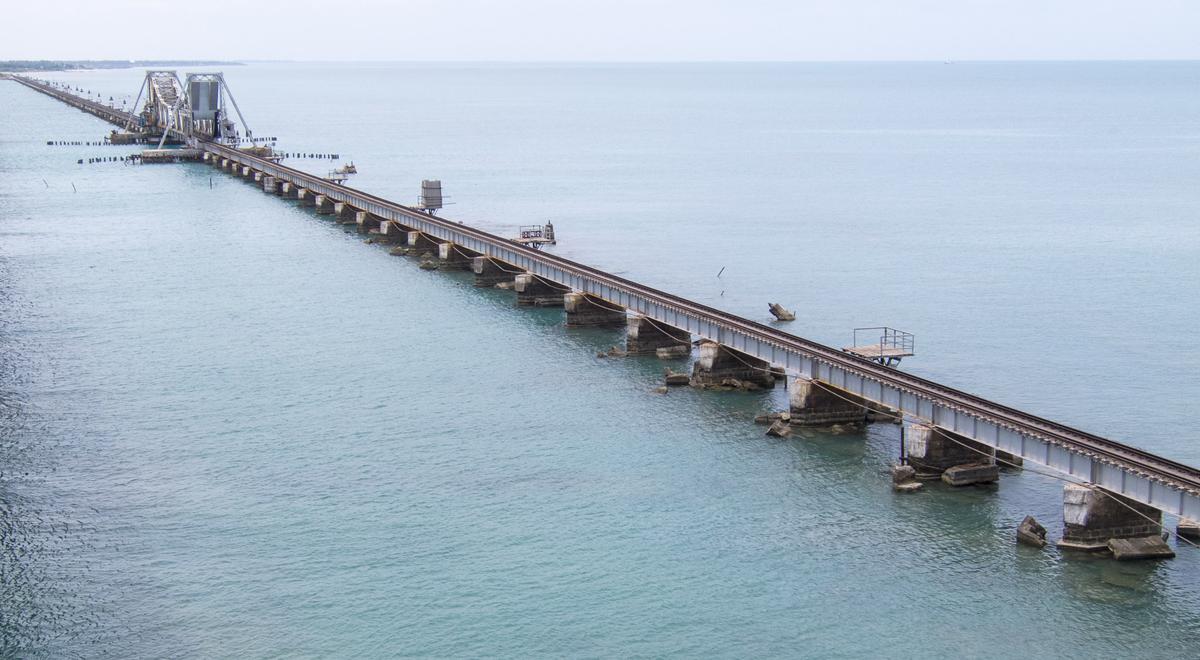
The Palk Strait, named after the British administrator Robert Palk, is a shallow body of water connecting the Bay of Bengal to the Gulf of Mannar. It is approximately 100 kilometers long and 14 to 60 kilometers wide, with an average depth of just 35 meters. The strait is dotted with numerous islands and shoals, most notably the Adam’s Bridge, a chain of limestone shoals that once formed a land bridge connecting India and Sri Lanka.
Historical Crossroads
The Palk Strait has been a vital maritime route for centuries, facilitating trade and cultural exchange between India and Sri Lanka. Its shallow waters and numerous islands provided safe havens for boats and ships, making it a crucial link for transporting goods like spices, textiles, and precious stones.
The region also holds immense historical and religious significance. The Palk Strait is believed to be the location of the legendary Rama Setu, or Adam’s Bridge, mentioned in the Hindu epic Ramayana. This mythical bridge, said to have been constructed by the vanara army led by Lord Rama, is believed to have enabled Rama’s journey to rescue Sita from the demon king Ravana. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was inhabited by various civilizations, including the Chola, Pandya, and Pallava dynasties, who left behind remnants of their rich history in the form of temples, forts, and ancient settlements.
Ecological Significance
The Palk Strait is a haven for biodiversity, boasting a rich marine ecosystem that supports a wide range of species. The region is home to numerous coral reefs, seagrass meadows, and mangrove forests, providing vital habitats for fish, crustaceans, sea turtles, and marine mammals. The strait also acts as a crucial breeding ground for several endangered species, including the dugong, a large marine mammal, and the green sea turtle.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts
Despite its ecological importance, the Palk Strait faces various challenges, including overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Overfishing has depleted fish stocks, threatening the livelihoods of local fishermen and the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem. Habitat destruction through coastal development, dredging, and oil spills has degraded coral reefs and seagrass meadows, disrupting the natural habitat of marine life. Pollution from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste poses a serious threat to the health of the ecosystem and the marine life it supports. Climate change, with its rising sea temperatures and increased ocean acidification, further exacerbates these challenges, threatening the very existence of the Palk Strait’s unique biodiversity.
Recognizing the importance of protecting this fragile ecosystem, several conservation efforts are underway. The Indian and Sri Lankan governments have established marine protected areas within the Palk Strait, aiming to regulate fishing activities, protect vulnerable species, and restore damaged habitats. NGOs and local communities are also actively involved in conservation efforts, promoting sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and raising awareness about the importance of preserving the Palk Strait’s unique ecosystem.
FAQs
1. What is the Palk Strait?
The Palk Strait is a narrow stretch of water separating India and Sri Lanka, connecting the Bay of Bengal to the Gulf of Mannar.
2. Why is the Palk Strait important?
The Palk Strait holds historical, economic, and ecological significance. It has been a vital maritime route for centuries, is a crucial fishing ground for local communities, and is home to a diverse marine ecosystem.
3. What are the major challenges facing the Palk Strait?
The Palk Strait faces challenges like overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, which threaten its delicate ecosystem and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
4. What are the conservation efforts underway to protect the Palk Strait?
Governments, NGOs, and local communities are working together to establish marine protected areas, promote sustainable fishing practices, reduce pollution, and raise awareness about the importance of preserving the Palk Strait’s unique ecosystem.
5. What is the Adam’s Bridge?
Adam’s Bridge is a chain of limestone shoals located in the Palk Strait, believed to have once formed a land bridge connecting India and Sri Lanka. It is also known as Rama Setu, a mythical bridge mentioned in the Hindu epic Ramayana.
Tips
1. Support sustainable fishing practices: Choose seafood that is sustainably sourced and avoid purchasing fish from areas known for overfishing.
2. Reduce plastic waste: Use reusable bags, bottles, and containers to minimize plastic pollution that ends up in the ocean.
3. Educate yourself and others: Learn about the importance of the Palk Strait’s ecosystem and share your knowledge with others to promote conservation efforts.
4. Support organizations working to protect the Palk Strait: Donate to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to marine conservation and the protection of the Palk Strait’s unique ecosystem.
5. Advocate for responsible environmental policies: Support policies that promote sustainable fishing, reduce pollution, and protect marine habitats.
Conclusion
The Palk Strait stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of nature, history, and human activity. Its rich biodiversity, historical significance, and economic importance highlight the need for its continued preservation. By understanding the challenges it faces and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure that the Palk Strait remains a vital part of the Indian Ocean’s ecosystem and a source of wonder and inspiration for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Palk Strait: A Bridge Between Nations and a Gateway to History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!