Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Related Articles: Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 3.1 The Importance of Tracing Maps
- 3.2 Techniques for Tracing Maps
- 3.3 Tools and Materials for Tracing Maps
- 3.4 Applications of Tracing Maps
- 3.5 FAQs about Tracing Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Tracing Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool

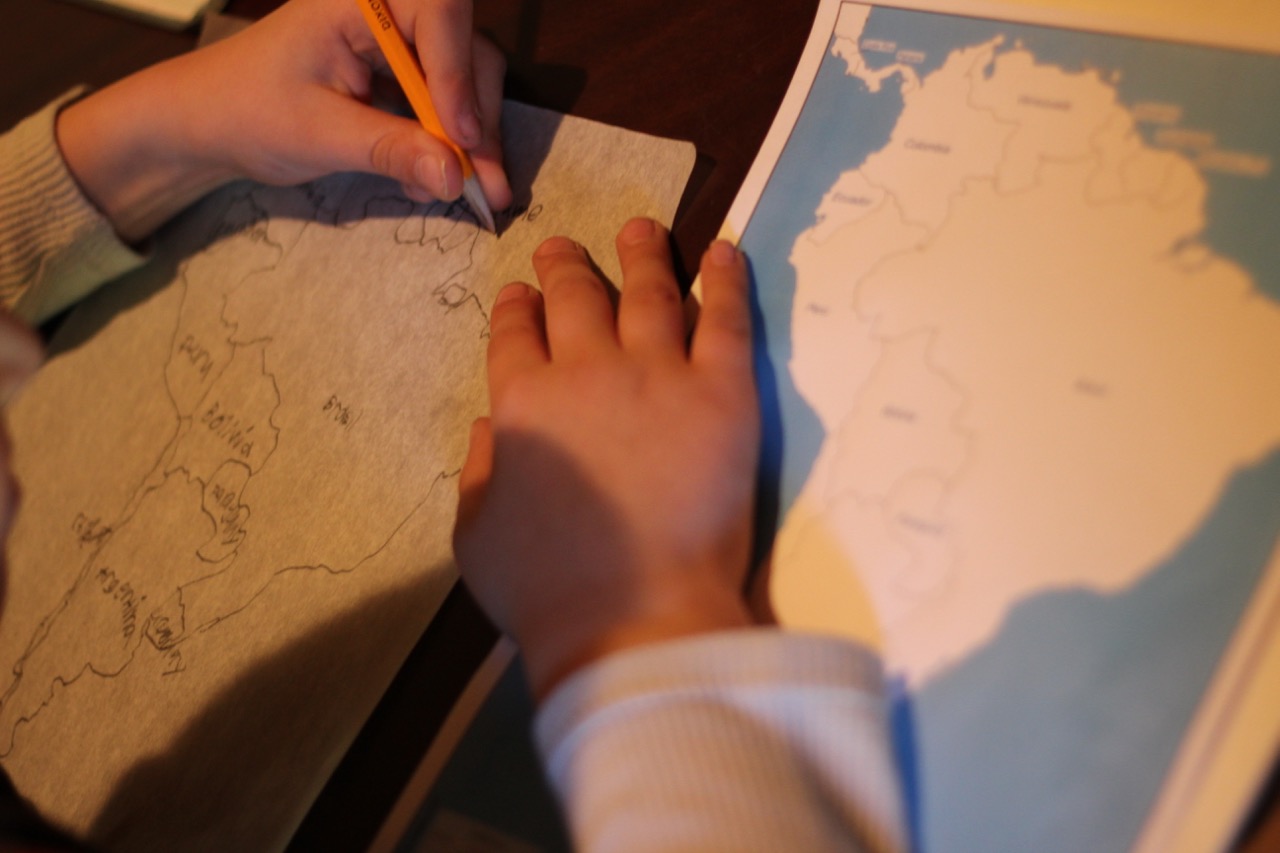
Tracing maps, a fundamental practice in cartography, geography, and various other fields, involves replicating the features of an existing map onto a separate surface. This process, often performed with the aid of tracing paper, allows for the creation of accurate copies, the modification of existing maps, or the extraction of specific details for further analysis. While the technology behind mapmaking has evolved significantly, the act of tracing remains a valuable skill, offering unique benefits and applications.
The Importance of Tracing Maps
Tracing maps serves a multitude of purposes, ranging from educational activities to professional applications. Here are some key reasons why tracing maps remains a relevant and valuable practice:
- Creating Copies: Tracing provides a straightforward method for replicating maps, preserving their original details and ensuring accuracy. This is particularly crucial for archival purposes, educational materials, or professional projects where maintaining the integrity of the map is paramount.
- Modifying Existing Maps: Tracing allows for the alteration of existing maps by adding or removing features, changing scale, or adjusting the layout. This flexibility is valuable for adapting maps to specific needs, highlighting particular areas of interest, or incorporating new information.
- Extracting Specific Details: By tracing specific sections of a map, users can isolate and focus on particular features, such as roads, landmarks, or geographical boundaries. This process simplifies analysis, facilitates comparison, and allows for the creation of specialized maps for specific purposes.
- Developing Spatial Skills: Tracing maps encourages the development of spatial reasoning and map interpretation skills. The act of replicating map features fosters an understanding of scale, distance, and relative location, enhancing spatial awareness and analytical abilities.
- Historical and Archival Value: Tracing maps is essential for preserving historical maps and documents. By creating copies, researchers can study and analyze these materials without risking damage to the originals, ensuring their preservation for future generations.
Techniques for Tracing Maps
The process of tracing maps involves a series of steps, each contributing to the accuracy and quality of the final product. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the techniques involved:
- Preparation: Begin by gathering the necessary materials, including the original map, tracing paper, pencils, and a light source. Ensure the map is laid flat and secured to prevent movement.
- Tracing: Position the tracing paper over the original map, securing it with weights or tape. Use a pencil to carefully trace the map features, paying attention to detail and accuracy.
- Transferring Details: Once the tracing is complete, transfer the details to a separate surface if required. This can involve using a pen or marker to create a permanent copy or using a computer to digitize the tracing for further manipulation.
- Labeling and Annotation: Add labels, annotations, or other relevant information to the traced map as needed. This enhances clarity and provides context for the map’s contents.
- Review and Refinement: Review the traced map for accuracy, completeness, and clarity. Make any necessary adjustments or refinements to ensure the final product meets the desired standards.
Tools and Materials for Tracing Maps
While the basic principles of tracing remain consistent, the specific tools and materials used can vary depending on the project and desired outcome. Here’s a list of common tools and materials used in tracing maps:
- Tracing Paper: A thin, translucent paper designed for tracing. Choose tracing paper with a smooth surface for optimal accuracy.
- Pencils: Use pencils with varying levels of hardness, allowing for different line weights and detail.
- Markers: Use markers to create permanent lines on the tracing, ideal for creating finished maps or for highlighting specific features.
- Light Table: A light table provides a bright, even light source for tracing, enhancing visibility and detail.
- Scanner: Use a scanner to digitize the traced map, allowing for further manipulation and analysis in digital formats.
- Computer Software: Several software programs are available for creating and editing maps, including specialized mapping applications and general image editing software.
Applications of Tracing Maps
Tracing maps find applications across diverse fields, contributing to various tasks and projects. Here are some examples:
- Education: Tracing maps is a valuable tool in classrooms, allowing students to learn about geography, history, and other subjects. Students can trace maps to understand spatial relationships, create their own maps, or modify existing maps to explore different scenarios.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use tracing maps to analyze city layouts, plan infrastructure development, and assess the impact of proposed projects. Tracing allows for modifications and adjustments to existing maps, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Environmental Studies: Environmental researchers use tracing maps to study ecosystems, track changes in land use, or analyze the spread of pollution. Tracing allows for the creation of specialized maps highlighting specific environmental features or trends.
- Historical Research: Historians use tracing maps to study historical maps, analyze the evolution of landscapes, or track the movement of people and goods. Tracing allows for the preservation of historical maps and the extraction of valuable information.
- Military Applications: Military personnel use tracing maps for planning operations, navigating terrain, and tracking enemy movements. Tracing allows for the creation of specialized maps tailored to specific military needs.
FAQs about Tracing Maps
Q: What are the benefits of tracing maps?
A: Tracing maps offers numerous benefits, including creating accurate copies, modifying existing maps, extracting specific details, developing spatial skills, and preserving historical maps.
Q: What are the different types of tracing paper?
A: Tracing paper comes in various types, including transparent, translucent, and opaque. The choice depends on the desired level of transparency and the type of map being traced.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when tracing maps?
A: Common mistakes include tracing over existing lines instead of outlining them, using a pencil that is too hard or too soft, and not securing the tracing paper properly.
Q: How can I ensure accurate tracing?
A: To ensure accurate tracing, use a sharp pencil, pay attention to detail, and double-check the tracing against the original map.
Q: What are some alternative methods for replicating maps?
A: Alternatives to tracing include scanning and digitizing maps, using photocopiers, or employing specialized mapping software.
Tips for Tracing Maps
- Use a Sharp Pencil: A sharp pencil ensures precise lines and accurate details.
- Secure the Tracing Paper: Ensure the tracing paper is securely attached to the original map to prevent movement.
- Light Source: Utilize a light table or other light source to enhance visibility and detail.
- Check for Accuracy: Regularly compare the tracing to the original map to ensure accuracy.
- Label and Annotate: Add labels and annotations to enhance clarity and provide context.
- Use Different Line Weights: Employ different pencil grades or markers to create varying line weights and highlight specific features.
- Practice: Tracing maps requires practice to develop proficiency and accuracy.
Conclusion
Tracing maps, a time-honored practice, remains an essential tool in various fields. Its ability to create copies, modify maps, extract details, and develop spatial skills makes it a valuable technique for education, professional applications, and historical preservation. By understanding the techniques, tools, and applications of tracing maps, individuals can effectively utilize this practice to enhance their understanding of maps and their significance. As technology continues to evolve, the act of tracing maps will likely remain a fundamental practice, adapting to new tools and techniques while preserving its core values of accuracy, precision, and spatial understanding.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tracing Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!