Unlocking Canada’s Climate: A Deep Dive into the Current Temperature Map
Related Articles: Unlocking Canada’s Climate: A Deep Dive into the Current Temperature Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Canada’s Climate: A Deep Dive into the Current Temperature Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Canada’s Climate: A Deep Dive into the Current Temperature Map

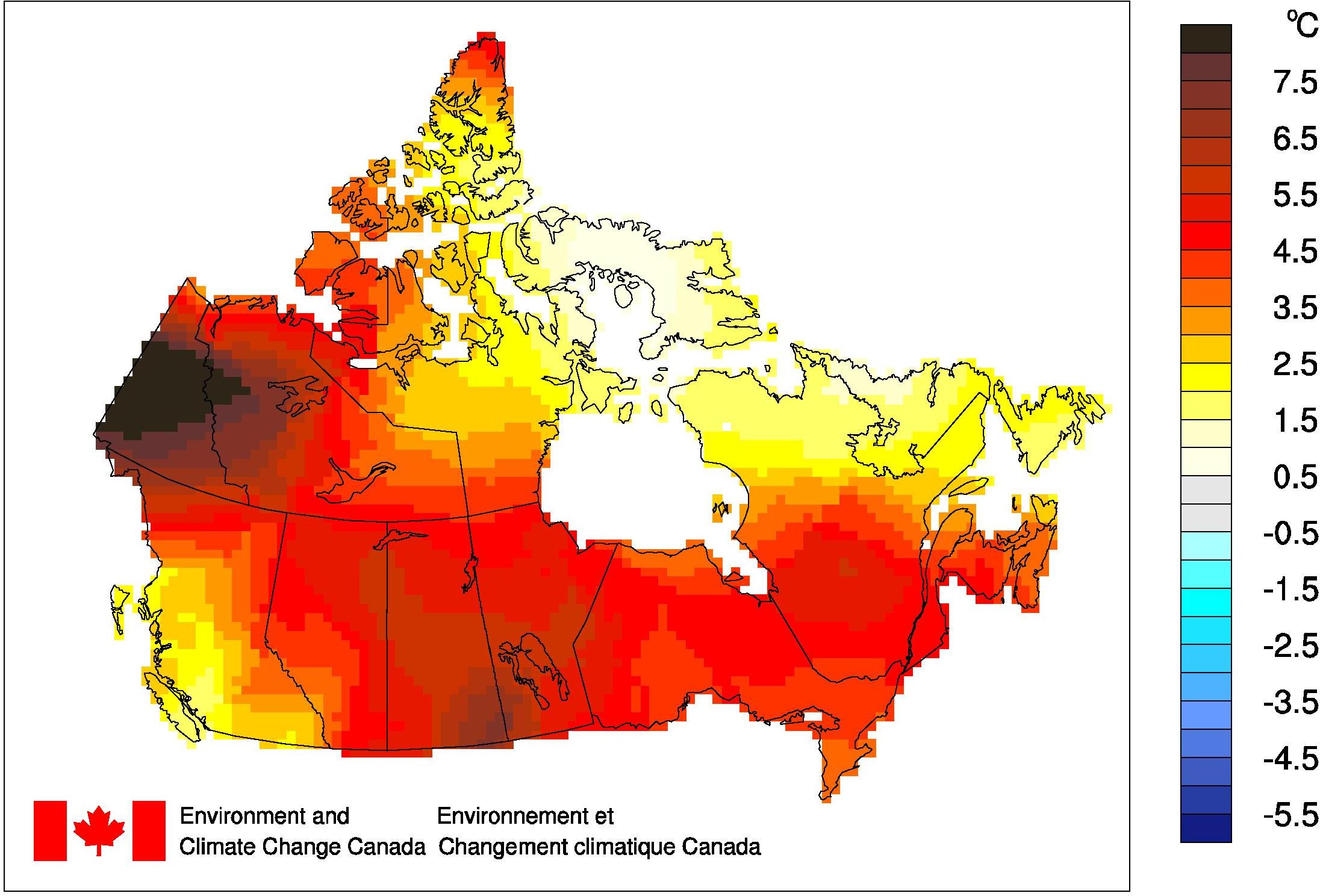
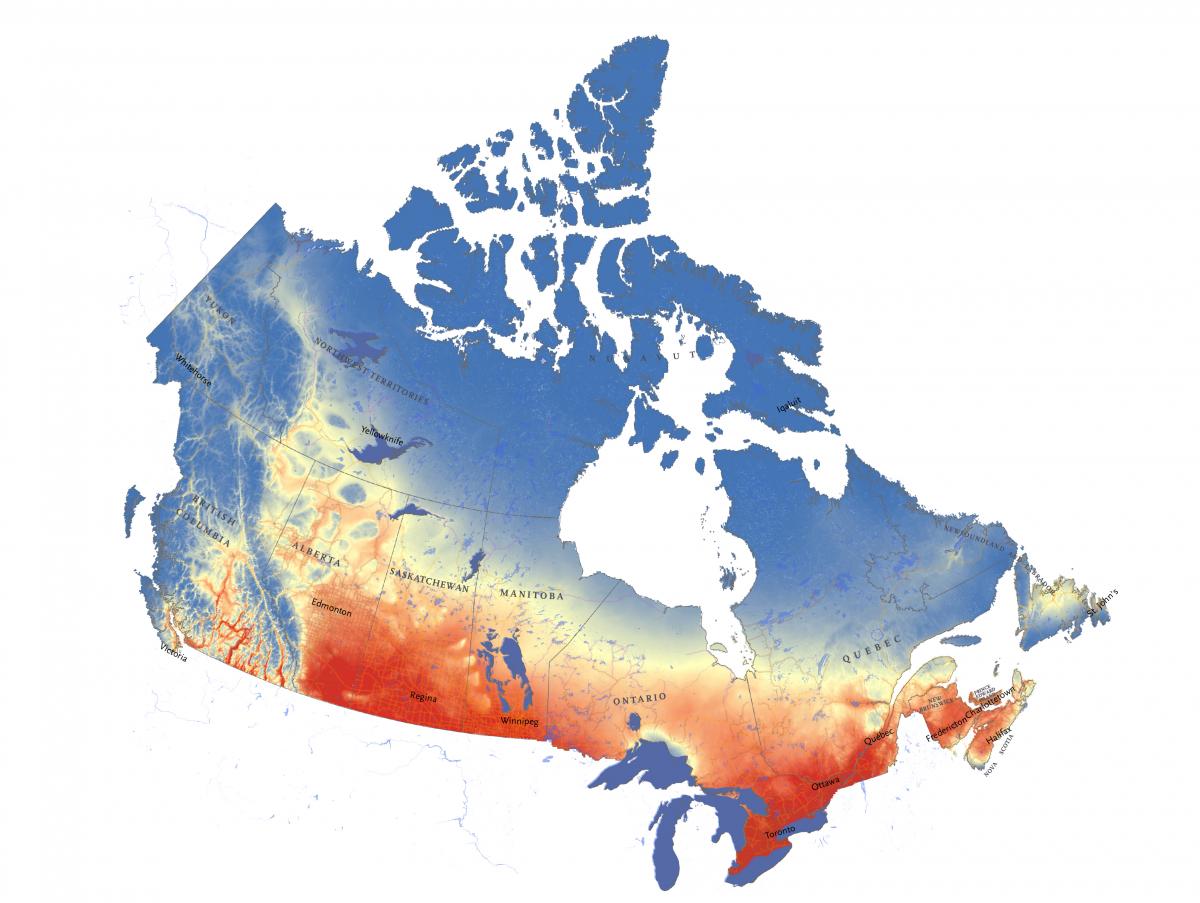
Canada, a vast and diverse nation spanning multiple climate zones, experiences a wide range of temperatures throughout the year. Understanding these temperature fluctuations is crucial for various aspects of life, from daily planning to long-term environmental monitoring. The current temperature map of Canada provides a snapshot of these variations, offering invaluable insights into the nation’s climate and its implications.
Understanding the Temperature Map
The current temperature map of Canada is a visual representation of the temperature across the country at a specific moment in time. It utilizes color gradients to depict temperature variations, with warmer colors indicating higher temperatures and cooler colors representing lower temperatures. This visual representation allows for a quick and intuitive understanding of the current temperature landscape across the vast Canadian geography.
Data Sources and Accuracy
Temperature data for the current map is sourced from various meteorological stations and weather monitoring networks across Canada. These stations gather real-time data on air temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other weather parameters. The data is then processed and displayed on the map, providing a reliable representation of current temperatures.
Factors Influencing Temperature Variations
Several factors contribute to the diverse temperature patterns observed across Canada. These include:
- Latitude: Canada’s vast geographical expanse stretches from the 49th to the 83rd parallel north, resulting in significant variations in solar radiation and daylight hours. Higher latitudes receive less direct sunlight, leading to colder temperatures.
- Proximity to Water: Coastal areas experience milder temperatures due to the moderating effect of large bodies of water. The Pacific Ocean, for example, influences the coastal climate of British Columbia, while the Atlantic Ocean influences the maritime provinces.
- Elevation: Higher elevations generally experience colder temperatures due to the thinner atmosphere and reduced air pressure. The mountainous regions of the Rockies and the Canadian Shield exhibit significant temperature differences compared to lower-lying areas.
- Air Masses: The movement of different air masses across Canada influences temperature patterns. Warm air masses from the south bring warmer temperatures, while cold air masses from the north result in cooler temperatures.
Importance and Applications
The current temperature map of Canada holds significant importance for various sectors and individuals:
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists utilize temperature data to develop accurate weather forecasts, providing essential information for public safety, transportation, and agriculture.
- Environmental Monitoring: The temperature map helps monitor climate change trends, revealing patterns of warming or cooling over time. This information is crucial for understanding the impact of climate change on ecosystems, infrastructure, and human health.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on temperature data to make informed decisions regarding planting, harvesting, and crop management. Accurate temperature information helps optimize crop yields and minimize potential losses due to extreme weather conditions.
- Tourism and Recreation: Travelers and outdoor enthusiasts use temperature maps to plan their activities, choosing destinations based on preferred weather conditions.
- Public Health: Temperature information is vital for public health officials to monitor heatwaves and cold snaps, issuing warnings and providing guidance to vulnerable populations.
Navigating the Temperature Map
Understanding the nuances of the temperature map requires familiarity with its key features:
- Color Legend: The map typically includes a color legend that translates the color gradient to corresponding temperature ranges.
- Temperature Units: Temperatures are usually displayed in Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the specific map source.
- Time Stamps: The map should indicate the time at which the data was collected, ensuring the information reflects the current temperature conditions.
- Data Source: The map should clearly identify the source of the temperature data, allowing users to assess the reliability of the information.
FAQs about the Current Temperature Map of Canada
Q: What is the best source for accessing the current temperature map of Canada?
A: Several reputable sources provide accurate and up-to-date temperature maps for Canada, including:
- Environment Canada: The official website of the Canadian government’s meteorological agency offers comprehensive weather data and maps.
- The Weather Network: A popular private weather forecasting service provides detailed weather information, including temperature maps.
- Google Maps: Google Maps integrates real-time weather data, including temperature, allowing users to view the current temperature map overlaid on the map interface.
Q: How often is the temperature map updated?
A: Temperature data is typically updated every hour or even more frequently, depending on the source and the specific location.
Q: Can I find historical temperature data on the map?
A: While the current temperature map focuses on real-time data, many sources also offer historical temperature data archives, allowing users to analyze trends and patterns over time.
Q: What are the limitations of the temperature map?
A: It’s important to note that the temperature map represents a snapshot of conditions at a specific moment in time. The temperature can vary significantly over short distances and time periods. Additionally, the map provides average temperatures for specific locations, not necessarily reflecting the exact temperature at a particular point.
Tips for Utilizing the Temperature Map
- Consider the time of day: Temperatures can vary significantly throughout the day, so it’s crucial to check the map for the most accurate reflection of current conditions.
- Compare with historical data: Analyze historical temperature data to understand long-term trends and potential climate variations.
- Combine with other weather information: Integrate temperature data with other weather parameters, such as wind speed, humidity, and precipitation, for a more comprehensive understanding of current conditions.
- Utilize the map for planning: Utilize the map to plan outdoor activities, travel arrangements, and other endeavors based on preferred weather conditions.
Conclusion
The current temperature map of Canada serves as a valuable tool for understanding the nation’s diverse climate and its implications for various aspects of life. By providing a visual representation of temperature variations across the country, the map empowers individuals, organizations, and government agencies to make informed decisions based on current weather conditions and to monitor long-term climate trends. Understanding the factors influencing temperature patterns and the proper interpretation of the map’s data are essential for maximizing its benefits and contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future for Canada.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Canada’s Climate: A Deep Dive into the Current Temperature Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!