Unlocking the Riches of Maine: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Heritage
Related Articles: Unlocking the Riches of Maine: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Heritage
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Riches of Maine: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Heritage. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Riches of Maine: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Heritage

Maine, renowned for its rugged coastline, dense forests, and picturesque towns, holds a hidden treasure beneath its surface: a rich geological history that has shaped the state’s landscape and economy. While the state’s gold rush days are long gone, the geological map of Maine continues to be a vital tool for understanding the state’s resources, environmental challenges, and potential for future development.
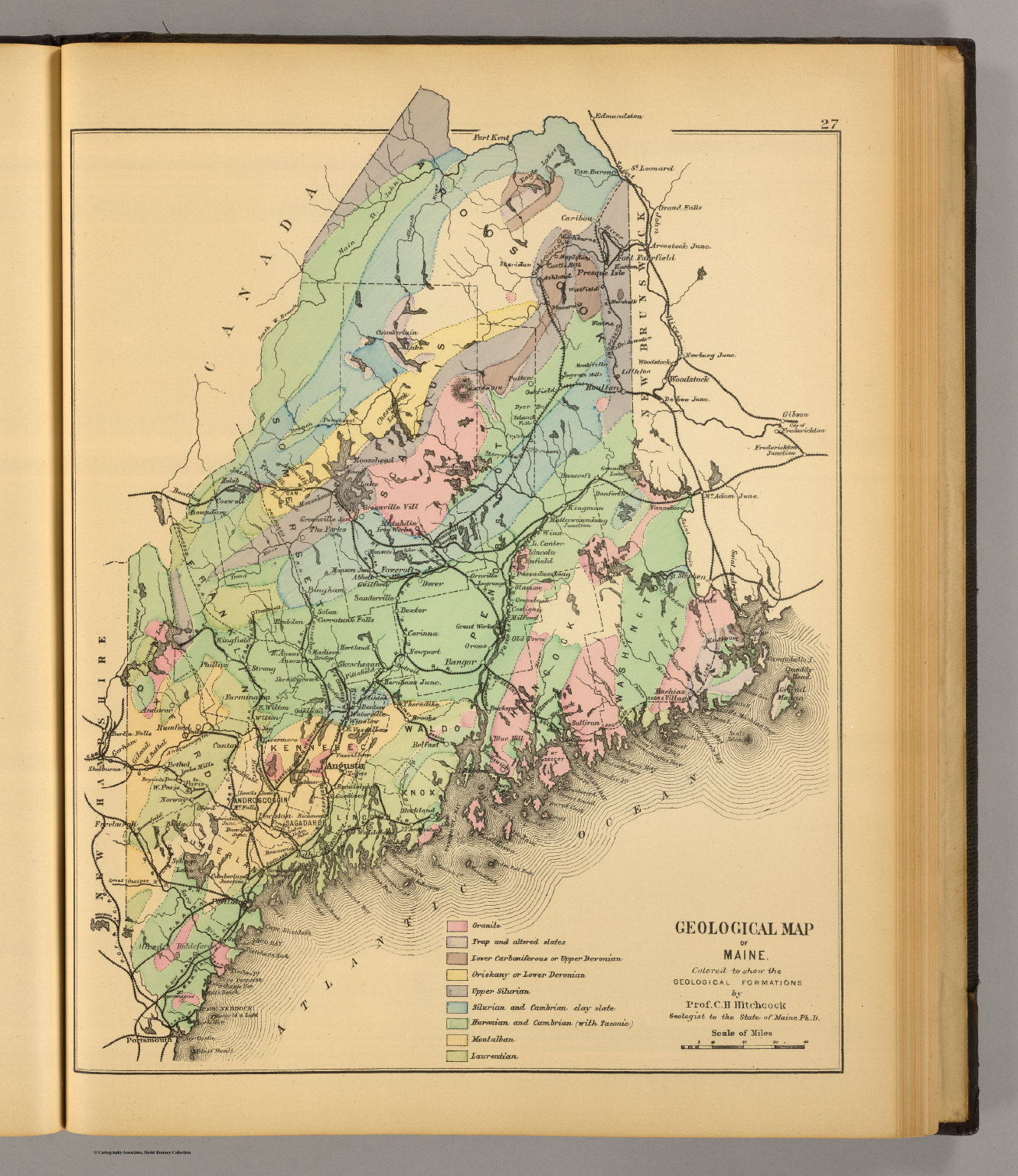
The Geological Map: A Window into Maine’s Past
The geological map of Maine is a visual representation of the state’s bedrock geology, showcasing the different rock types and their ages, spanning billions of years. This intricate tapestry of geological formations reveals a fascinating story of Earth’s history, from the ancient Precambrian era to the more recent glacial periods.
The Importance of the Geological Map
The geological map serves as a vital reference for various sectors, including:
- Natural Resource Exploration: The map helps pinpoint potential locations for mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and groundwater resources. This information is crucial for mining, energy extraction, and water management.
- Environmental Protection: Understanding the geological makeup of the state aids in identifying areas susceptible to pollution, erosion, and other environmental hazards. This knowledge is critical for developing sustainable land management practices.
- Infrastructure Development: The map assists in selecting suitable locations for building roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects, minimizing risks associated with geological instability.
- Scientific Research: The geological map serves as a fundamental tool for researchers studying geological processes, climate change, and Earth’s history.
- Education and Outreach: The map provides a visual representation of the state’s geological heritage, fostering public understanding and appreciation for Earth sciences.
Deciphering the Geological Map: A Closer Look
The geological map is a complex document that requires some interpretation to fully understand its significance. Here are some key features:
- Rock Types: The map identifies various rock types, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Each type has unique characteristics that influence its use and environmental impact.
- Geological Formations: The map outlines specific geological formations, such as faults, folds, and intrusions, which reveal the forces that shaped the state’s landscape.
- Age of Rocks: The map indicates the age of different rock formations, providing insights into the timeline of geological events.
- Mineral Deposits: The map highlights potential locations for mineral deposits, including gold, silver, copper, and other valuable resources.
Exploring Maine’s Geological Riches: A Journey through Time
The geological map of Maine offers a glimpse into a rich and diverse geological history. Some key features of the state’s geology include:
- The Precambrian Shield: The oldest rocks in Maine, dating back billions of years, are found in the north and west of the state. These rocks were formed during a time of intense volcanic activity and tectonic plate collisions.
- The Paleozoic Era: During this period, approximately 540 to 250 million years ago, the state was covered by shallow seas, leading to the formation of sedimentary rocks, including limestone, sandstone, and shale.
- The Mesozoic Era: This era, spanning 250 to 66 million years ago, saw the formation of igneous rocks associated with volcanic activity.
- The Cenozoic Era: The most recent era, beginning 66 million years ago, was marked by the uplift of the Appalachian Mountains and the advance and retreat of glaciers.
The Legacy of Maine’s Geological Heritage
The geological map of Maine is not just a scientific document; it’s a testament to the state’s natural heritage and its influence on its history, culture, and economy. From the granite quarries that supplied building materials for iconic structures to the geothermal energy potential harnessed from the Earth’s heat, Maine’s geology continues to shape its future.
FAQs about Maine’s Geological Map
Q: Where can I access the geological map of Maine?
A: The Maine Geological Survey (MGS) provides a variety of geological maps and data, including online versions and downloadable files. You can access these resources on the MGS website: https://www.maine.gov/dacf/mgs/
Q: What are some of the most important mineral deposits in Maine?
A: Maine is known for its deposits of granite, limestone, sand and gravel, and other industrial minerals. While gold deposits are historically significant, they are not commercially viable today.
Q: How does the geological map help in managing water resources?
A: The map helps identify aquifers, underground formations that store groundwater. This information is crucial for ensuring sustainable water supplies and protecting groundwater quality.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges related to Maine’s geology?
A: Maine faces challenges related to acid rain, coastal erosion, and the potential for seismic activity. The geological map helps identify areas vulnerable to these hazards.
Tips for Using the Geological Map
- Understand the Scale: The map’s scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
- Identify Key Features: Focus on specific geological formations, rock types, and mineral deposits of interest.
- Consult Additional Resources: Combine the geological map with other data sources, such as topographic maps and aerial photographs, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Seek Expert Guidance: If you need help interpreting the map or using it for specific purposes, consult with a geologist or other qualified professional.
Conclusion
The geological map of Maine is an invaluable resource for understanding the state’s rich geological history, its natural resources, and its environmental challenges. By studying the map and its intricate details, we gain a deeper appreciation for the forces that shaped Maine’s landscape and the potential it holds for future development. It serves as a reminder that Maine’s story is not only written on its surface but also etched deep within its geological foundation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Riches of Maine: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Heritage. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!