Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean
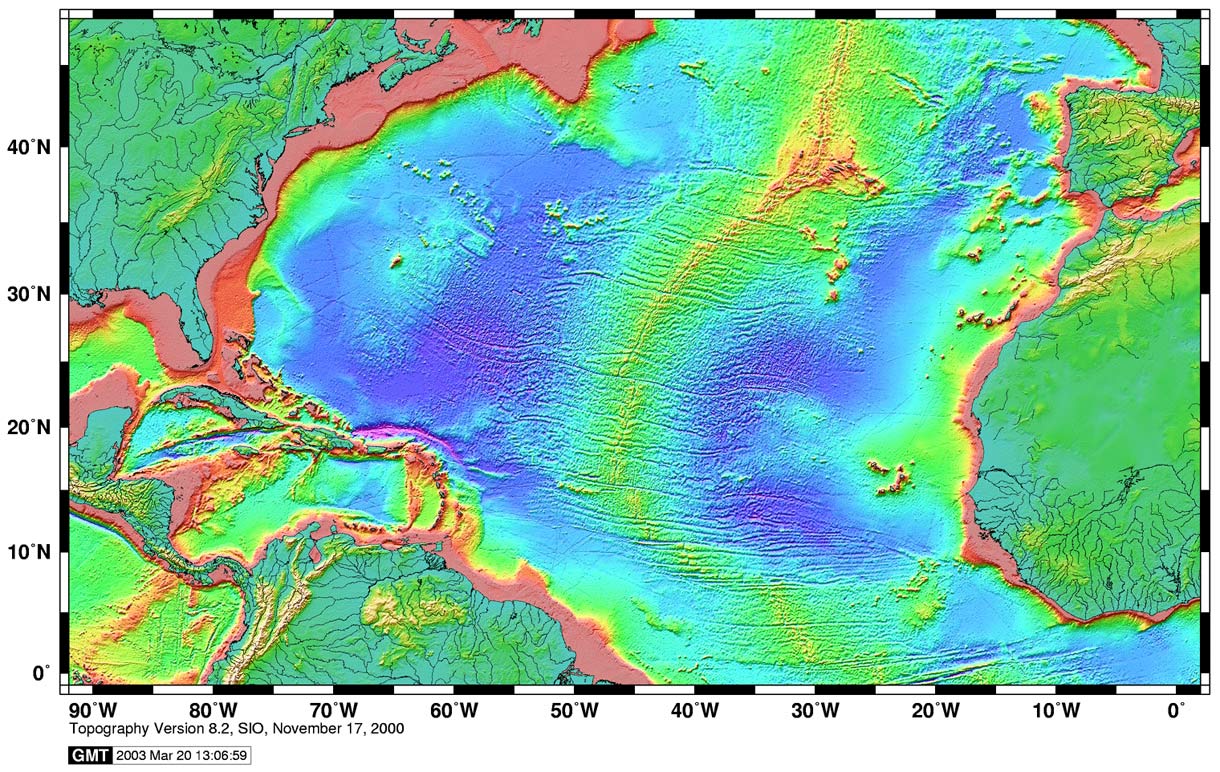
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering nearly 20% of the Earth’s surface, holds within its depths a captivating topography that reveals its intricate geological history and diverse ecosystems. Navigating this underwater landscape requires a specialized tool – the topographic map of the Atlantic Ocean. This map, a visual representation of the ocean floor’s elevation and features, provides invaluable insights into the ocean’s structure, its influence on marine life, and its vital role in global processes.
Understanding the Topography: A Visual Journey to the Ocean Floor
Topographic maps of the Atlantic Ocean utilize contour lines, similar to those found on land maps, to depict variations in elevation. These lines connect points of equal depth, effectively creating a three-dimensional representation of the ocean floor. The map reveals a dynamic landscape, punctuated by towering underwater mountains, deep trenches, vast plains, and extensive plateaus.
Key Features of the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography
-
Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This prominent underwater mountain range, traversing the Atlantic Ocean from north to south, is a testament to the theory of plate tectonics. It marks the boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates and the South American and African plates. The ridge is characterized by volcanic activity and hydrothermal vents, contributing to the ocean’s unique ecosystem.
-
Abyssal Plains: Stretching across vast areas of the ocean floor, these flat plains represent the deepest regions of the Atlantic. Formed by sediment accumulation over millions of years, they support a diverse range of marine life adapted to the extreme conditions of the deep ocean.
-
Ocean Trenches: These deep, narrow depressions mark the points where tectonic plates collide. The Puerto Rico Trench, reaching depths of over 8,600 meters, is a prime example. These trenches are often associated with intense seismic activity and are home to unique marine life.
-
Seamounts: Isolated underwater mountains, rising from the ocean floor, are often extinct volcanoes. These seamounts provide critical habitat for a variety of marine species, including corals, fish, and invertebrates.
-
Guyots: Flat-topped seamounts, formed by erosion and wave action, offer unique ecosystems and serve as potential sources of valuable resources.
The Significance of Topographic Maps: Unveiling the Ocean’s Secrets
The topographic map of the Atlantic Ocean serves as a crucial tool for understanding the ocean’s complex dynamics and its impact on global systems.
-
Navigation and Exploration: Maps provide essential information for marine navigation, enabling safe and efficient travel for ships and submarines. They also aid in exploration, guiding researchers to areas of interest for scientific study.
-
Resource Management: The map helps identify potential areas for resource extraction, including oil and gas deposits, mineral resources, and renewable energy sources. It also plays a role in sustainable fishing practices, ensuring the preservation of marine ecosystems.
-
Climate Change Research: The topography of the ocean floor influences ocean currents, which play a critical role in global climate regulation. Understanding these currents and their interaction with the ocean floor is essential for studying climate change impacts.
-
Biodiversity Conservation: Maps reveal the location of diverse marine habitats, including coral reefs, seamounts, and deep-sea trenches. This information is crucial for identifying and protecting vulnerable ecosystems and promoting sustainable management practices.
-
Geological Studies: The map provides insights into the geological history of the Atlantic Ocean, revealing the processes that shaped its current topography. This information is valuable for understanding plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and the evolution of Earth’s crust.
FAQs about the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean
Q: How are topographic maps of the Atlantic Ocean created?
A: Topographic maps are created using a combination of techniques, including sonar mapping, satellite imagery, and direct sampling. Sonar, which emits sound waves and measures their reflection, provides detailed information about the ocean floor’s shape. Satellite imagery captures surface features and helps create a broader context. Direct sampling involves collecting physical samples of the ocean floor, providing valuable data on its composition and geological history.
Q: What are the limitations of topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps, while valuable tools, have limitations. They are representations of the ocean floor based on available data, which may not always be complete or accurate. The resolution of maps can vary depending on the data collection methods used, and some areas may be poorly mapped due to logistical challenges or the presence of extreme conditions.
Q: How do topographic maps contribute to understanding the ocean’s role in climate change?
A: The ocean floor’s topography significantly influences ocean currents, which play a vital role in global climate regulation. Maps help identify key areas where currents interact with the ocean floor, providing insights into heat transfer, carbon sequestration, and the distribution of nutrients. This information is crucial for understanding the ocean’s role in climate change mitigation and adaptation.
Q: What are the potential benefits of using topographic maps for marine resource management?
A: Topographic maps are essential for sustainable resource management in the Atlantic Ocean. They help identify potential areas for resource extraction, such as oil and gas deposits and mineral resources. By revealing the location of sensitive marine habitats, maps can guide the development of responsible extraction practices, minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring the long-term health of the ocean ecosystem.
Q: How do topographic maps contribute to the protection of marine biodiversity?
A: Topographic maps provide valuable information about the distribution of marine habitats, including coral reefs, seamounts, and deep-sea trenches. This information is crucial for identifying and protecting vulnerable ecosystems, promoting sustainable fishing practices, and ensuring the long-term conservation of marine biodiversity.
Tips for Utilizing Topographic Maps of the Atlantic Ocean
-
Understand the Map’s Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail it provides. Larger-scale maps offer more precise information about smaller features, while smaller-scale maps provide a broader overview of the ocean floor.
-
Interpret Contour Lines: Contour lines represent lines of equal depth, indicating the elevation of the ocean floor. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope.
-
Analyze Map Features: Identify key features on the map, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, abyssal plains, ocean trenches, seamounts, and guyots. These features provide insights into the ocean’s geological history and the distribution of marine life.
-
Combine with Other Data Sources: Integrate topographic maps with other data sources, such as satellite imagery, oceanographic data, and biological surveys, to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the Atlantic Ocean.
Conclusion
The topographic map of the Atlantic Ocean is a powerful tool for understanding the ocean’s complex dynamics and its vital role in global systems. It provides a visual representation of the ocean floor’s topography, revealing a dynamic landscape of mountains, plains, trenches, and seamounts. This information is essential for navigation, resource management, climate change research, biodiversity conservation, and geological studies. By utilizing topographic maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the Atlantic Ocean’s intricate beauty and its profound impact on our planet.


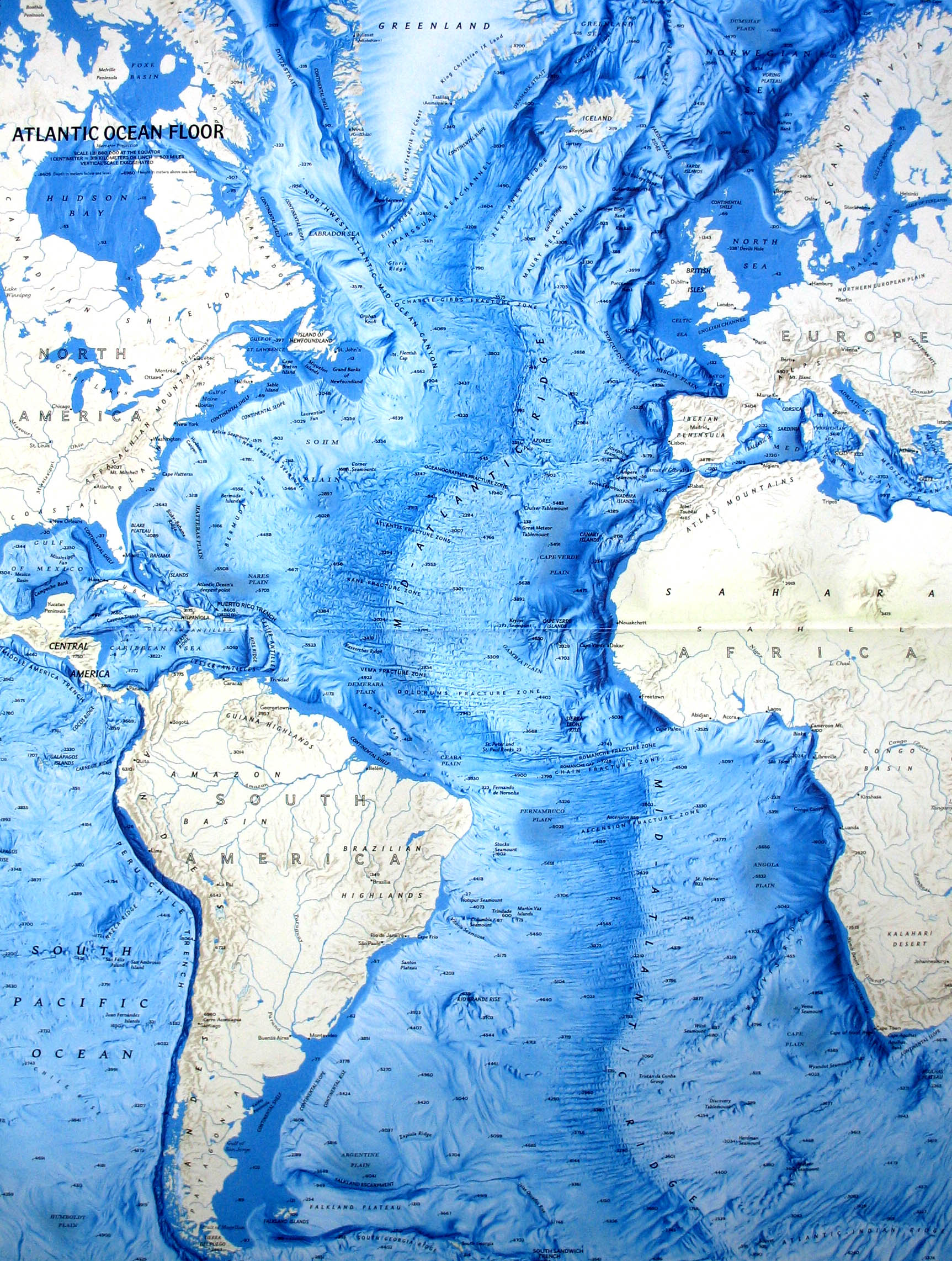
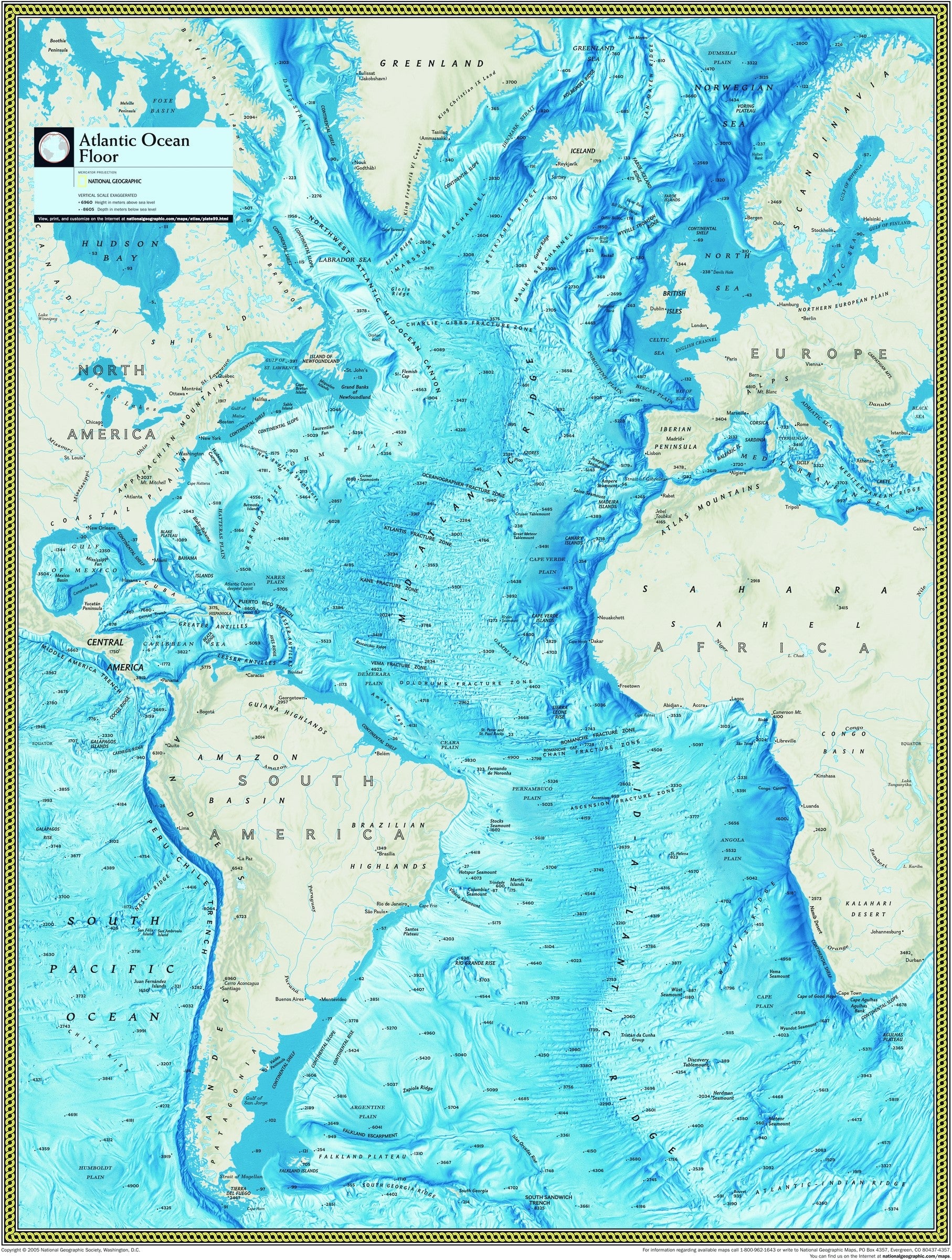
![]()
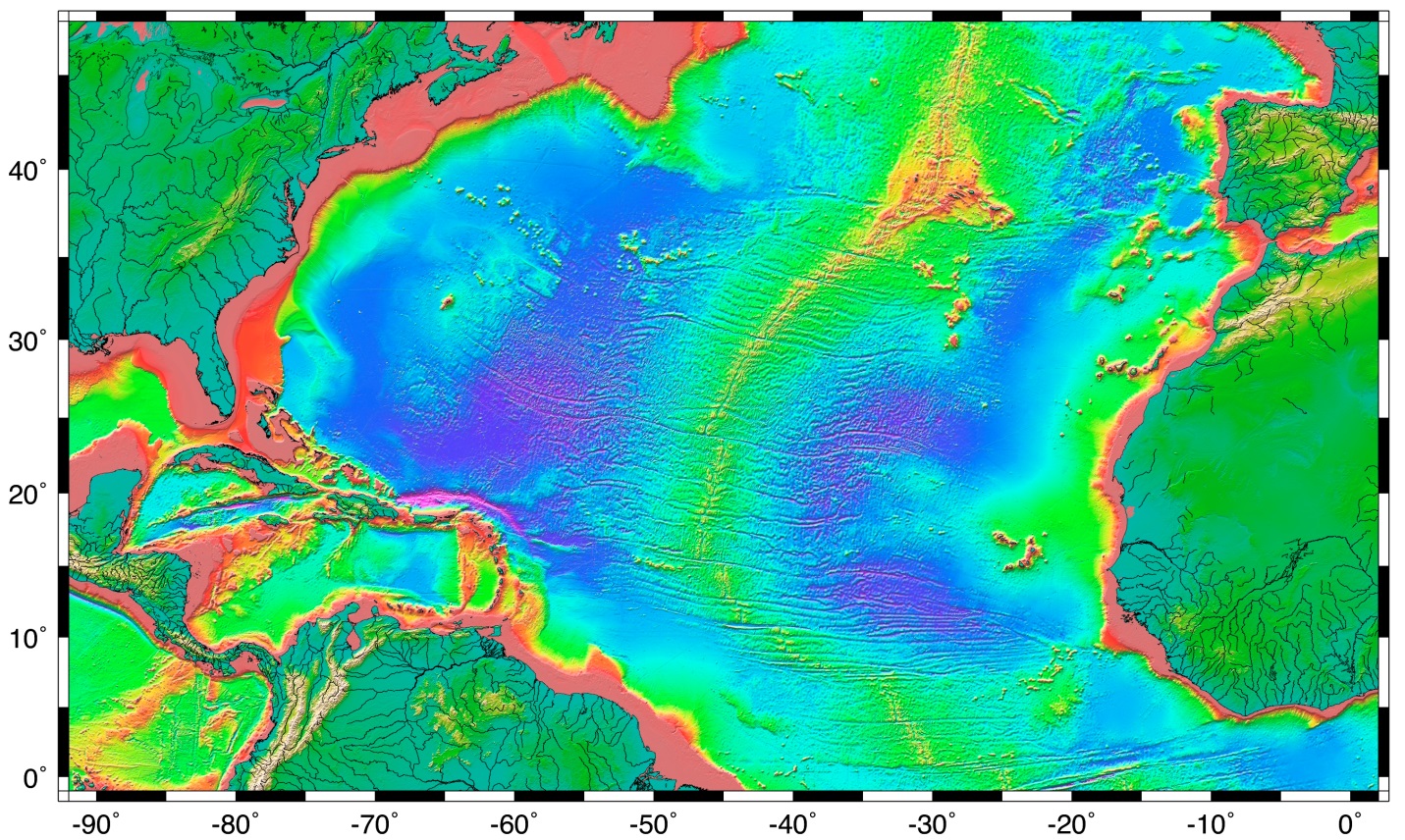
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of the Atlantic Ocean. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
