Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Oceania: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Oceania: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Oceania: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Oceania: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography
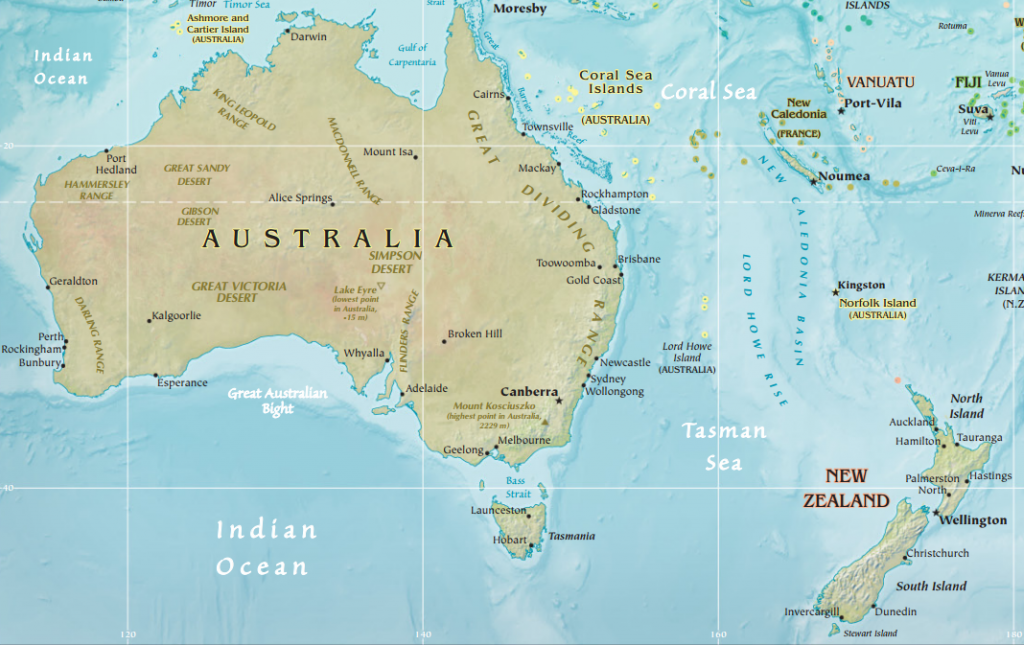
Oceania, a vast and geographically diverse region spanning the Pacific Ocean, comprises a constellation of islands, archipelagos, and continental landmasses. Understanding the physical geography of Oceania is essential for comprehending the region’s unique ecosystems, cultural diversity, and economic potential. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of Oceania’s physical map, highlighting its key features, geological processes, and the profound impact these have on human life and the environment.
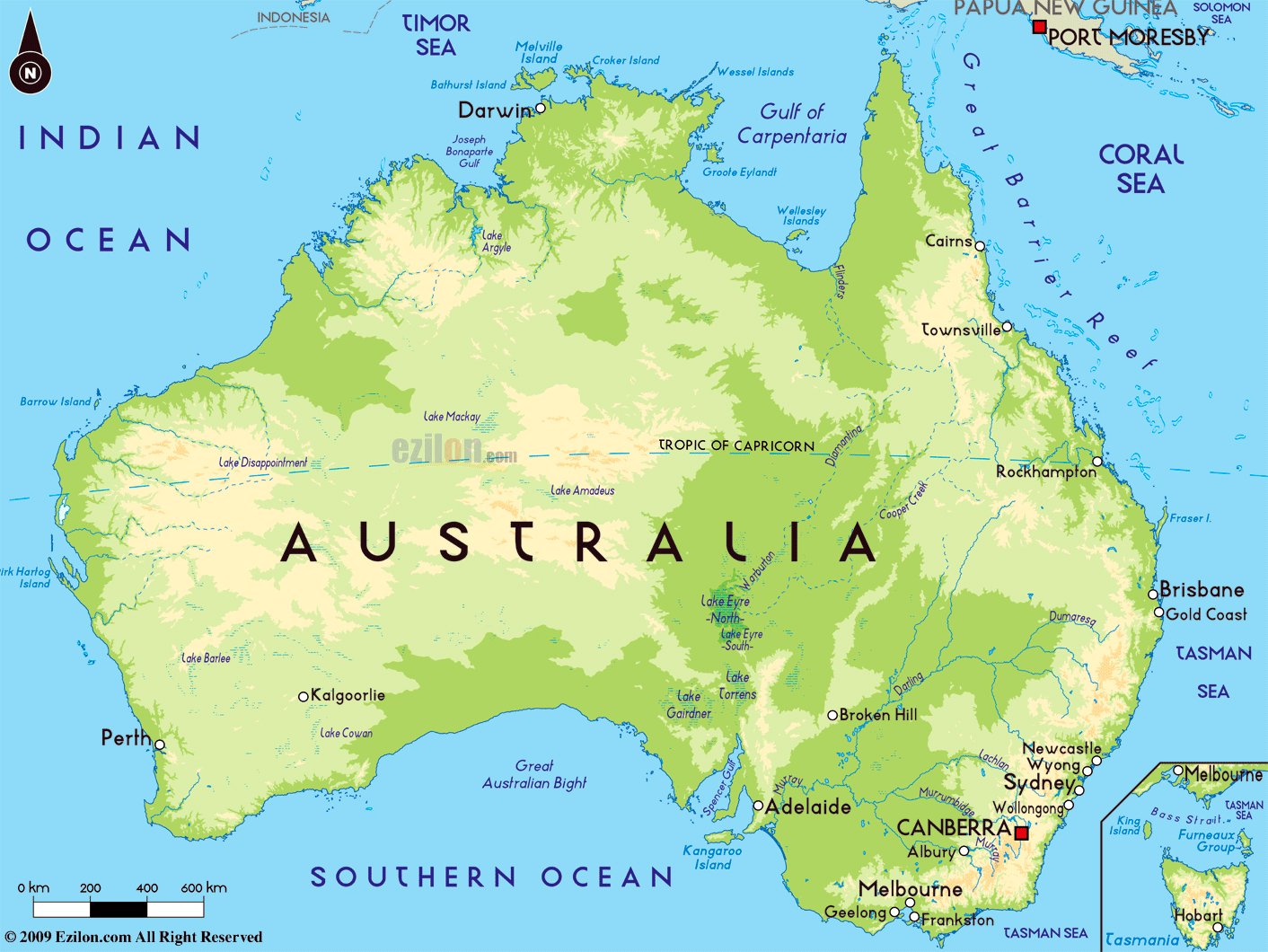
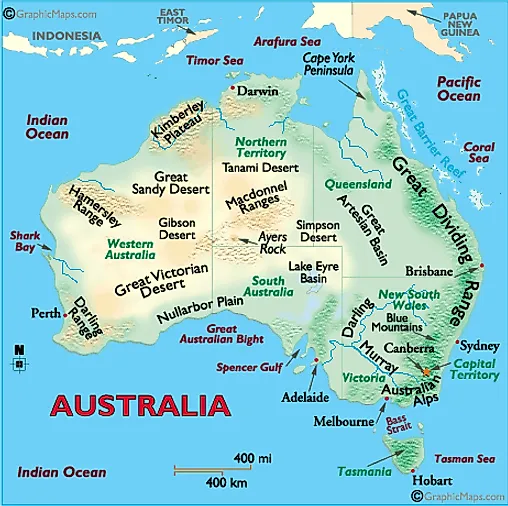
The Continental Island: Australia
The largest landmass in Oceania, Australia, is a continental island, formed by the breakup of the ancient supercontinent Gondwana millions of years ago. Its diverse landscape, ranging from the arid interior to the lush coastal regions, reflects its geological history and unique tectonic setting.
- The Great Dividing Range: This extensive mountain chain forms the eastern backbone of Australia, influencing rainfall patterns and creating diverse ecological zones.
- The Outback: The vast, arid interior of Australia, known as the Outback, is characterized by its unique flora and fauna adapted to harsh conditions.
- The Great Barrier Reef: This magnificent natural wonder, the world’s largest coral reef system, is a testament to the diverse marine life thriving in the region.
Island Chains: A Symphony of Volcanic and Coral Formations
Beyond Australia, Oceania encompasses numerous island chains, each with its distinct geological origins and physical characteristics.
- Volcanic Islands: Formed by volcanic activity, these islands rise from the ocean floor, often displaying dramatic landscapes with volcanic peaks, craters, and fertile soils. Examples include the islands of Hawaii, Fiji, and Vanuatu.
- Coral Islands: Constructed by the accumulation of coral skeletons over millennia, these islands are typically low-lying and vulnerable to rising sea levels. The atolls of the Pacific, such as those in the Marshall Islands and Tuvalu, are prime examples.
- Continental Fragments: Some islands in Oceania are fragments of the ancient Gondwana supercontinent, separated by tectonic forces. New Zealand, with its mountainous terrain and active volcanoes, is a prime example.
Tectonic Forces Shaping Oceania
The physical geography of Oceania is intricately linked to the dynamic forces of plate tectonics. The region sits at the convergence of several tectonic plates, leading to volcanic activity, earthquakes, and the formation of new landmasses.
- The Pacific Ring of Fire: This zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity encircles the Pacific Ocean, including many islands in Oceania.
- Subduction Zones: Where tectonic plates collide, one plate slides beneath the other, causing volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. The islands of Tonga and the Kermadec Islands are formed by subduction zones.
- Oceanic Hotspots: These areas of volcanic activity are located far from plate boundaries, creating chains of volcanic islands, such as the Hawaiian archipelago.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Oceania’s vast expanse and diverse physical features create a wide range of climates and weather patterns.
- Tropical Climates: Many islands in Oceania experience tropical climates with high temperatures, humidity, and abundant rainfall.
- Arid Climates: The interior of Australia experiences arid conditions with low rainfall and extreme temperatures.
- Temperate Climates: Some islands, like New Zealand, enjoy temperate climates with distinct seasons.
- Oceanic Influence: The surrounding ocean plays a significant role in regulating temperatures and influencing rainfall patterns.
Environmental Challenges and Opportunities
Oceania’s physical geography poses both challenges and opportunities for its inhabitants.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels threaten low-lying islands, while extreme weather events pose risks to coastal communities.
- Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and cyclones are recurring threats, requiring robust disaster preparedness strategies.
- Biodiversity: Oceania’s unique ecosystems support a rich array of endemic species, but habitat loss and invasive species threaten biodiversity.
- Natural Resources: The region’s diverse resources, including minerals, fisheries, and renewable energy sources, offer economic potential.
FAQs about Oceania’s Physical Map
1. What are the main landforms in Oceania?
Oceania’s landforms are diverse, encompassing continental islands like Australia, volcanic islands, coral islands, and continental fragments. Each landform type is shaped by unique geological processes and influences the region’s physical geography.
2. How does plate tectonics affect Oceania’s physical geography?
Oceania sits at the convergence of several tectonic plates, leading to volcanic activity, earthquakes, and the formation of new landmasses. This dynamic process shapes the region’s landscape and creates its distinct geological features.
3. What are the major climate zones in Oceania?
Oceania experiences a range of climates, from tropical to arid and temperate, influenced by its vast expanse, physical features, and oceanic currents.
4. What are the environmental challenges facing Oceania?
Oceania faces various environmental challenges, including climate change, natural disasters, biodiversity loss, and resource management issues. These challenges necessitate sustainable development strategies and international cooperation.
5. What are the economic opportunities presented by Oceania’s physical geography?
Oceania’s diverse resources, including minerals, fisheries, and renewable energy sources, offer economic opportunities. However, sustainable development practices are essential to ensure the long-term viability of these resources.
Tips for Understanding Oceania’s Physical Map
- Use a physical map: A detailed physical map of Oceania is essential for visualizing the region’s diverse landforms, elevation changes, and water bodies.
- Explore online resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive maps and satellite imagery, can provide valuable insights into Oceania’s physical geography.
- Read about the region’s geological history: Understanding the tectonic processes that shaped Oceania’s landforms is crucial for comprehending its physical characteristics.
- Consider the impact of climate: Climate patterns play a significant role in shaping Oceania’s ecosystems and influencing human activities.
- Engage with local communities: Exploring the region’s cultural heritage and traditional knowledge can deepen your understanding of the relationship between humans and the environment.
Conclusion
Oceania’s physical map is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped the region over millions of years. From the vast expanse of Australia to the intricate mosaic of islands scattered across the Pacific, Oceania’s physical geography is a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, geological processes, and cultural heritage. Understanding the region’s physical characteristics is crucial for appreciating its unique ecosystems, addressing environmental challenges, and harnessing its economic potential. By exploring the physical map of Oceania, we gain a deeper understanding of this remarkable region and its profound impact on the world.
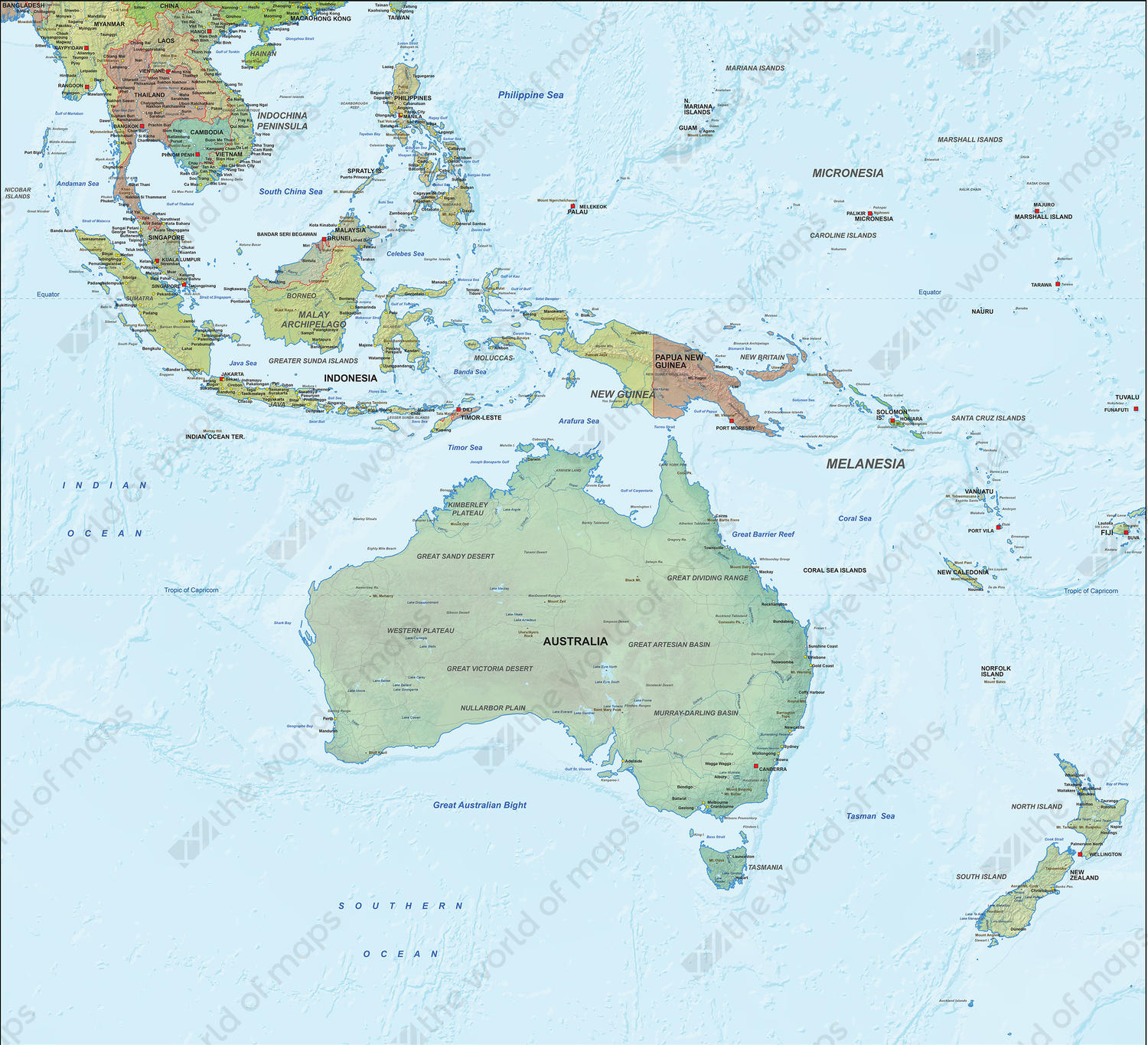

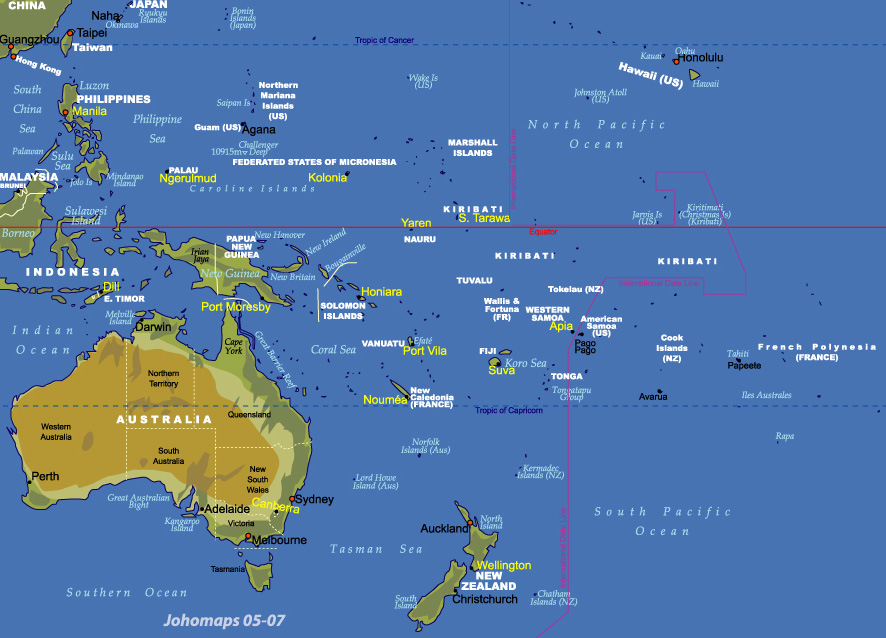
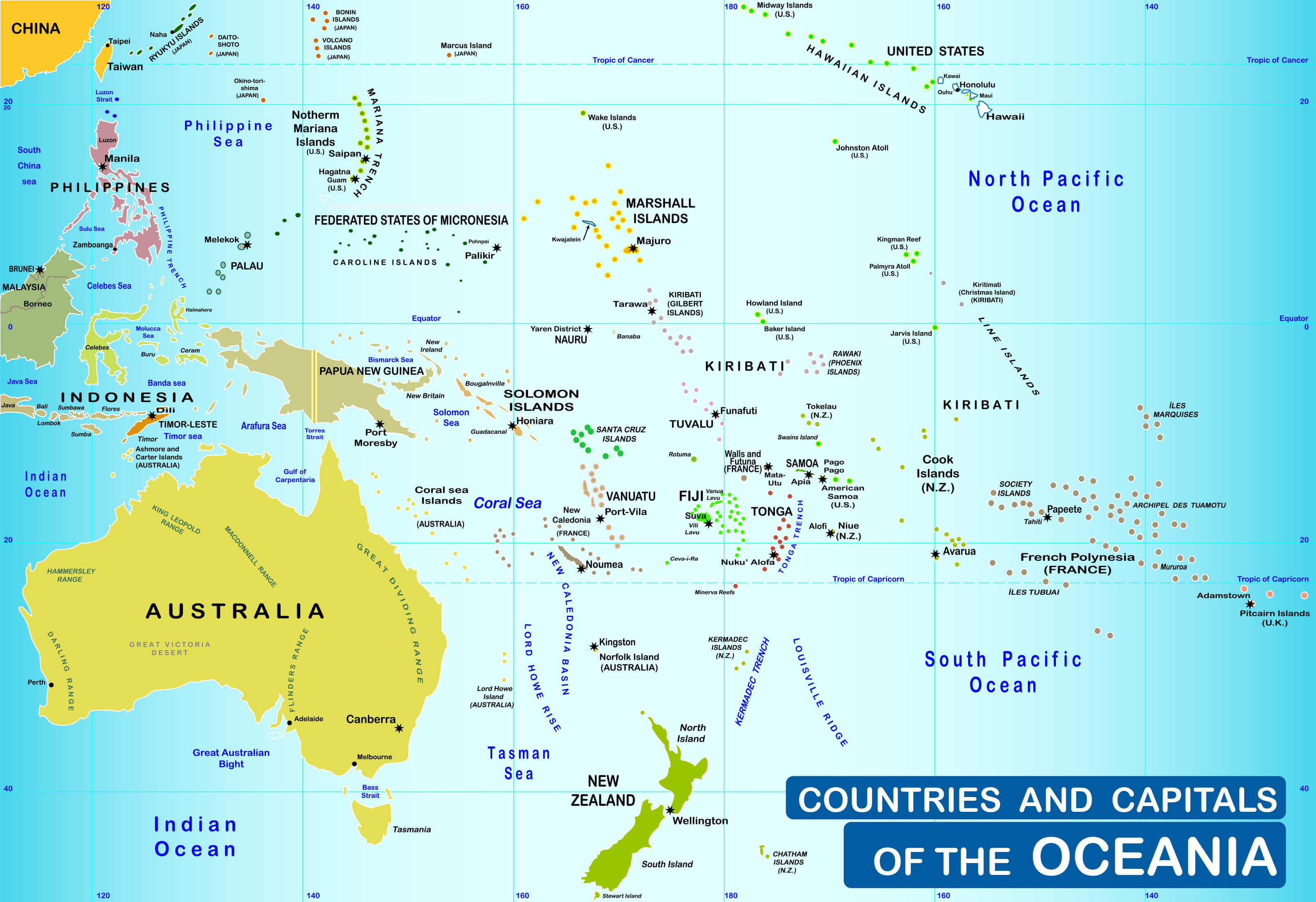

/Oceania-map_1-41000000-5ab126ce642dca0036965219.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Oceania: A Comprehensive Guide to its Physical Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!