Unveiling the Geography of the United States: A Deep Dive into the Contiguous 48
Related Articles: Unveiling the Geography of the United States: A Deep Dive into the Contiguous 48
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Geography of the United States: A Deep Dive into the Contiguous 48. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Geography of the United States: A Deep Dive into the Contiguous 48

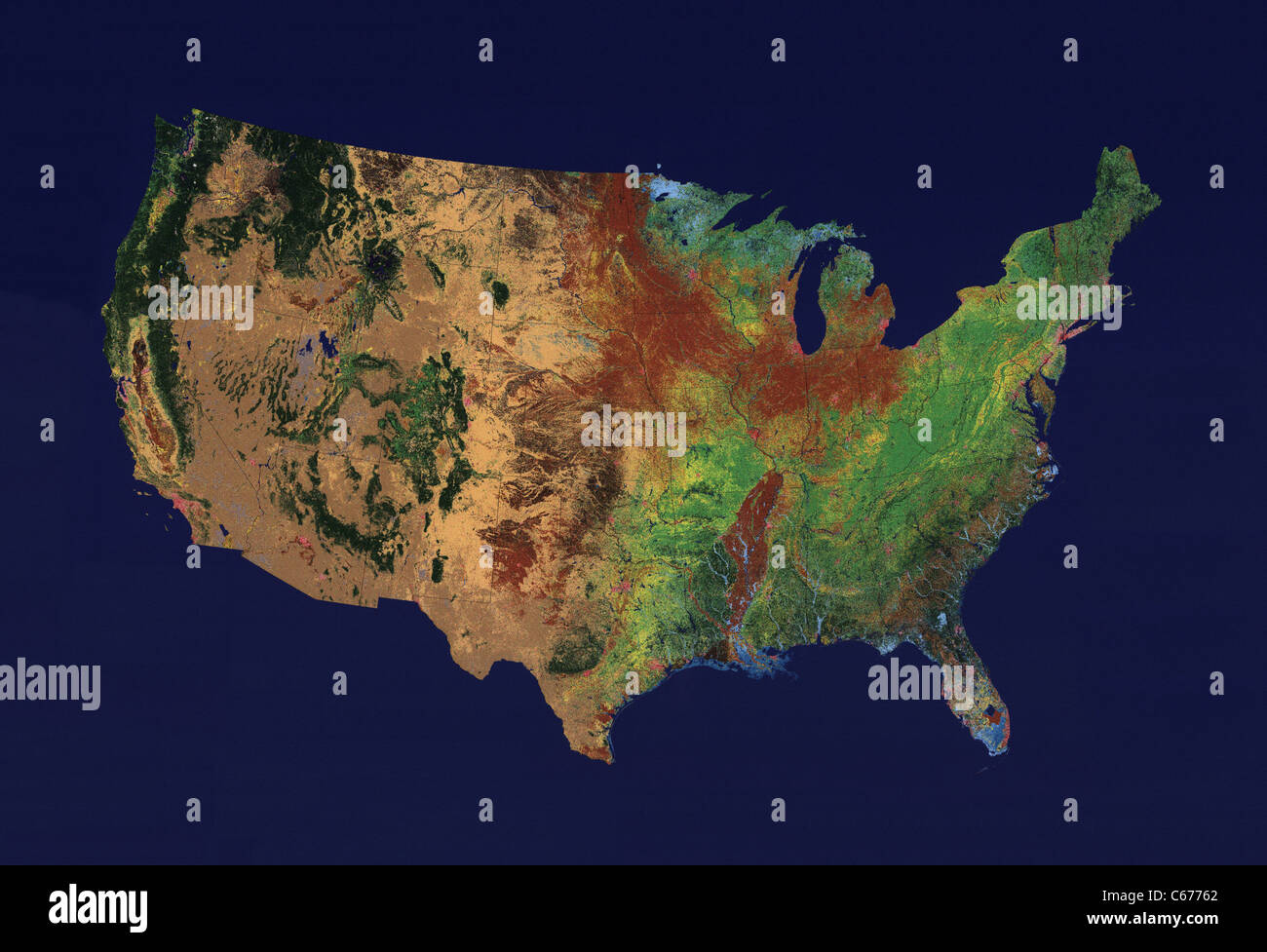
The United States of America, a nation of vast landscapes and diverse cultures, comprises 50 states, each with its unique identity. While Alaska and Hawaii are geographically separated, the contiguous United States, often referred to as the "Lower 48," forms a cohesive geographic entity that plays a crucial role in the nation’s history, economy, and cultural fabric. This article delves into the intricacies of the contiguous United States map, exploring its geographical features, historical significance, and ongoing relevance.
The Physical Landscape: A Tapestry of Diverse Regions
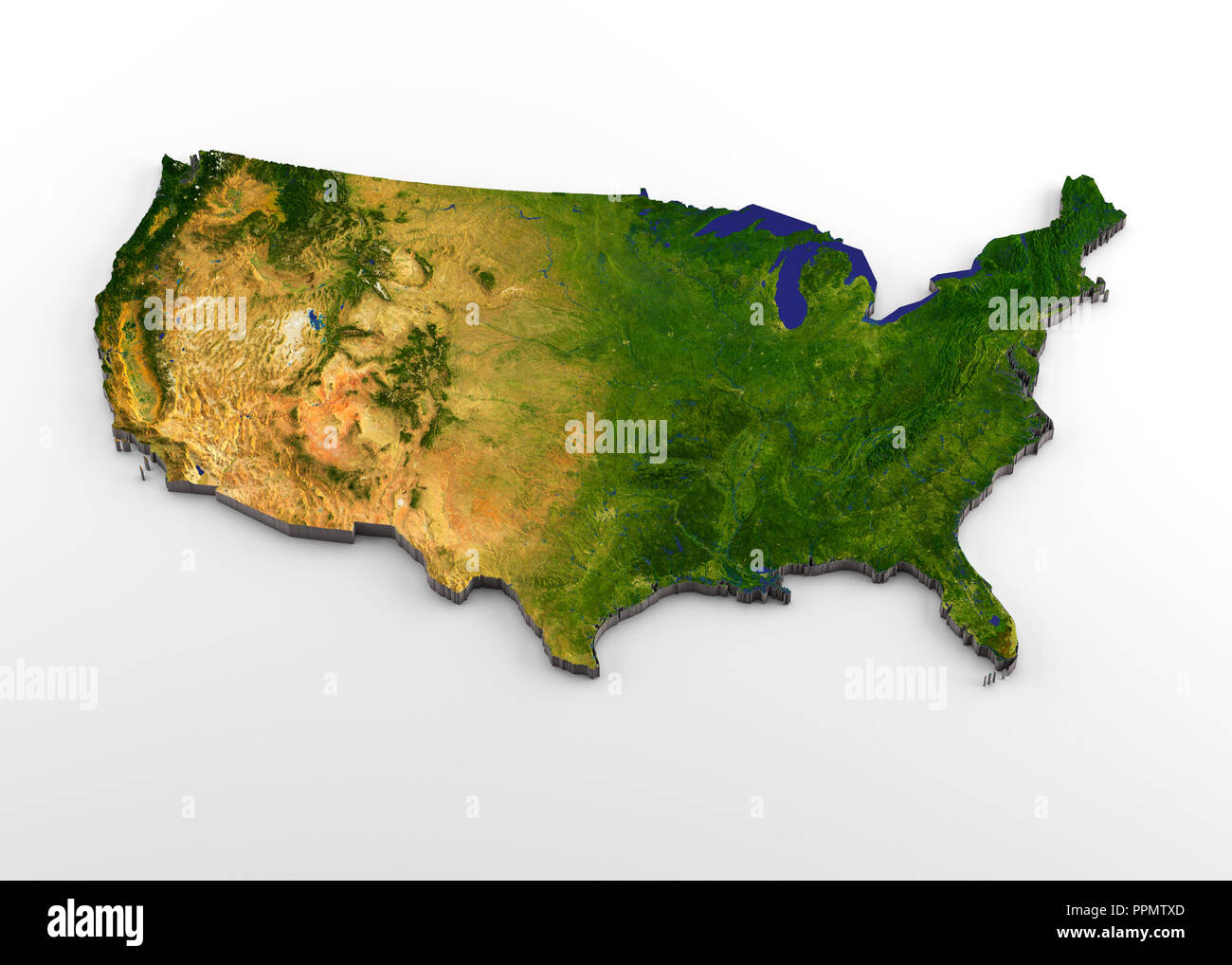
The contiguous United States map presents a diverse panorama of geographical features, encompassing mountains, deserts, forests, plains, and vast coastlines.
-
The Rocky Mountains: This majestic range, stretching from Canada to Mexico, forms the western spine of the contiguous United States. Its snow-capped peaks, rugged canyons, and alpine meadows offer breathtaking scenery and serve as a vital watershed for the region.
-
The Great Plains: Rolling grasslands and fertile farmlands define the Great Plains, extending eastward from the Rockies. This vast expanse, once home to Native American tribes, now supports a significant agricultural industry, providing the nation with essential food resources.
-
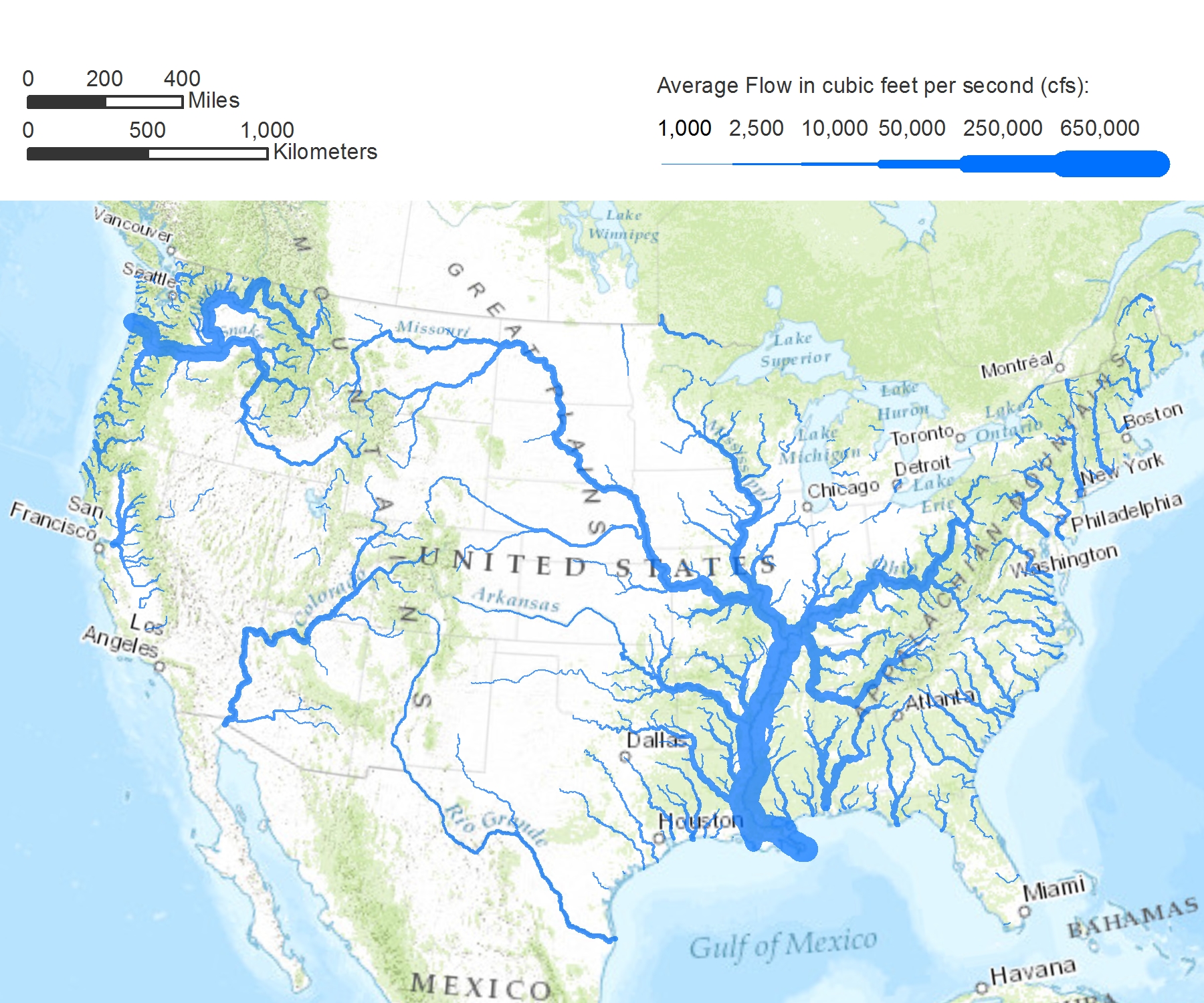
The Mississippi River: This mighty waterway, flowing from Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico, serves as a vital transportation route and a source of economic activity. Its vast watershed encompasses a significant portion of the contiguous United States, fostering biodiversity and supporting a diverse range of ecosystems.
-
The Appalachian Mountains: These ancient mountains, stretching from Alabama to Maine, offer a stark contrast to the western plains. Their rugged terrain, forested slopes, and scenic valleys provide a haven for diverse wildlife and attract outdoor enthusiasts.
-
The Coastal Regions: The contiguous United States boasts extensive coastlines along the Atlantic, Pacific, and Gulf of Mexico. These regions, rich in natural resources and cultural heritage, have played a pivotal role in the nation’s development, shaping its trade, industry, and cultural identity.
Historical Significance: A Nation Forged by Geography
The contiguous United States map is not just a geographical representation; it embodies a nation’s history, revealing the path of westward expansion and the evolution of its cultural identity.
-
The Louisiana Purchase: This pivotal acquisition in 1803 doubled the size of the United States, extending its territory westward to the Rocky Mountains. The Louisiana Purchase opened up vast expanses of land for settlement, contributing to the nation’s westward expansion and agricultural development.
-
The Manifest Destiny: This 19th-century belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent fueled the westward movement. The contiguous United States map reflects this historical narrative, showcasing the gradual westward expansion of the nation’s borders.
-
The Civil War: The geographical divide between the North and the South, evident on the contiguous United States map, played a crucial role in the outbreak and course of the Civil War. The conflict, ultimately resolved through the abolition of slavery, reshaped the nation’s social and political fabric.
Contemporary Relevance: A Framework for Understanding the Nation
The contiguous United States map remains a relevant tool for understanding the nation’s contemporary socio-economic landscape.
-
Economic Hubs: The contiguous United States map highlights the concentration of economic activity in major metropolitan areas. From the financial center of New York City to the tech hub of Silicon Valley, these urban centers drive the nation’s economy and influence its cultural trends.
-
Infrastructure and Transportation: The contiguous United States map reveals the network of highways, railroads, and waterways that connect the nation’s cities and towns. These transportation systems facilitate trade, commerce, and the movement of people, underpinning the nation’s economic growth.
-
Environmental Challenges: The contiguous United States map underscores the interconnectedness of the nation’s environment. Issues like climate change, water scarcity, and pollution transcend state boundaries, requiring a collaborative approach to address these challenges.
FAQs: A Closer Look at the Contiguous United States
1. What is the largest state in the contiguous United States?
The largest state in the contiguous United States is Texas, with a land area of 268,596 square miles.
2. What are the major geographical features of the contiguous United States?
The major geographical features include the Rocky Mountains, the Great Plains, the Mississippi River, the Appalachian Mountains, and the coastal regions.
3. How did the contiguous United States map evolve over time?
The map has evolved through westward expansion, acquisitions of territory, and the admission of new states.
4. What are the major economic hubs in the contiguous United States?
Major economic hubs include New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, San Francisco, and Houston.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing the contiguous United States?
Environmental challenges include climate change, water scarcity, air pollution, and deforestation.
Tips for Understanding the Contiguous United States Map
-
Use online interactive maps: Numerous websites offer interactive maps that allow users to zoom in on specific areas, explore geographical features, and access additional information.
-
Study historical maps: Examining historical maps provides insights into the evolution of the contiguous United States map and its historical significance.
-
Explore regional differences: Researching the unique characteristics of each region, from its climate and natural resources to its cultural heritage, helps develop a comprehensive understanding of the contiguous United States.
-
Connect geography to current events: Analyzing current events through the lens of geography reveals how geographical factors influence political, economic, and social issues.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Geography and Progress
The contiguous United States map is more than a visual representation of landmass; it embodies a nation’s history, its cultural diversity, and its ongoing evolution. Understanding the geographical features, historical context, and contemporary relevance of the contiguous United States map provides a deeper appreciation for the nation’s past, present, and future. As the United States continues to grapple with challenges and opportunities, the map serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of its people, its resources, and its place in the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Geography of the United States: A Deep Dive into the Contiguous 48. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!