Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours
- 3.1 Deciphering the Language of Contours
- 3.2 The Power of Contour Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.3 Beyond Visual Representation: The Importance of Contour Maps
- 3.4 Understanding Contour Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions: Deciphering the Language of Contours
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Language of Landscape
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours
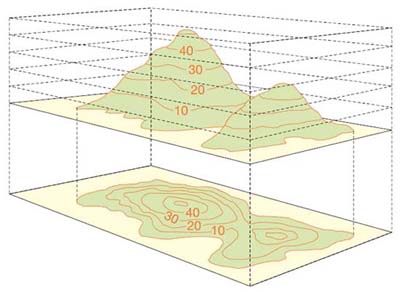
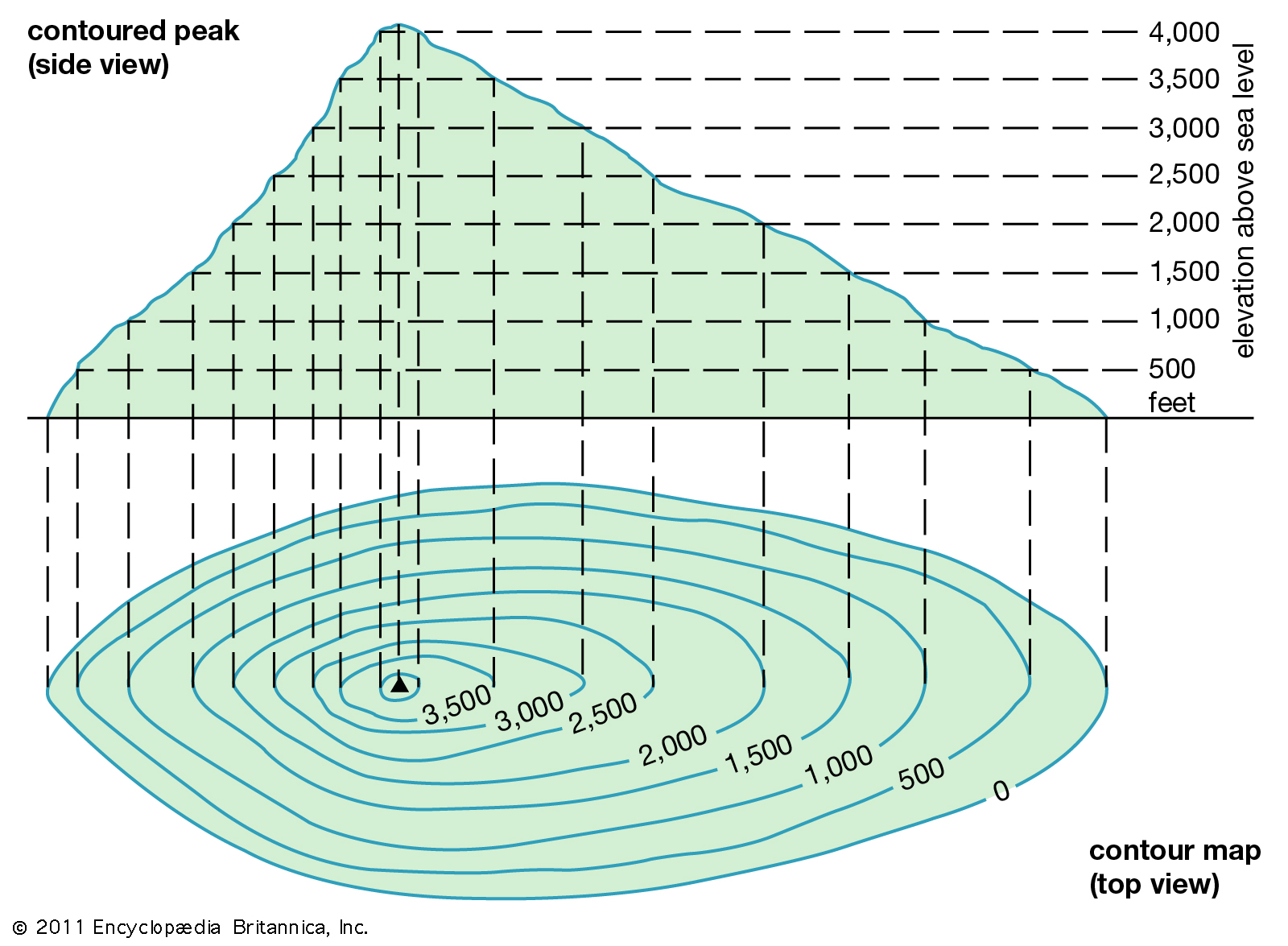
Maps are invaluable tools for navigating the world, providing visual representations of geographic features and locations. However, a standard map often fails to convey the crucial element of terrain – the ups and downs, the hills and valleys that shape the landscape. This is where maps with elevation contours come into play, offering a powerful visual language to understand the three-dimensional nature of the earth’s surface.
Deciphering the Language of Contours
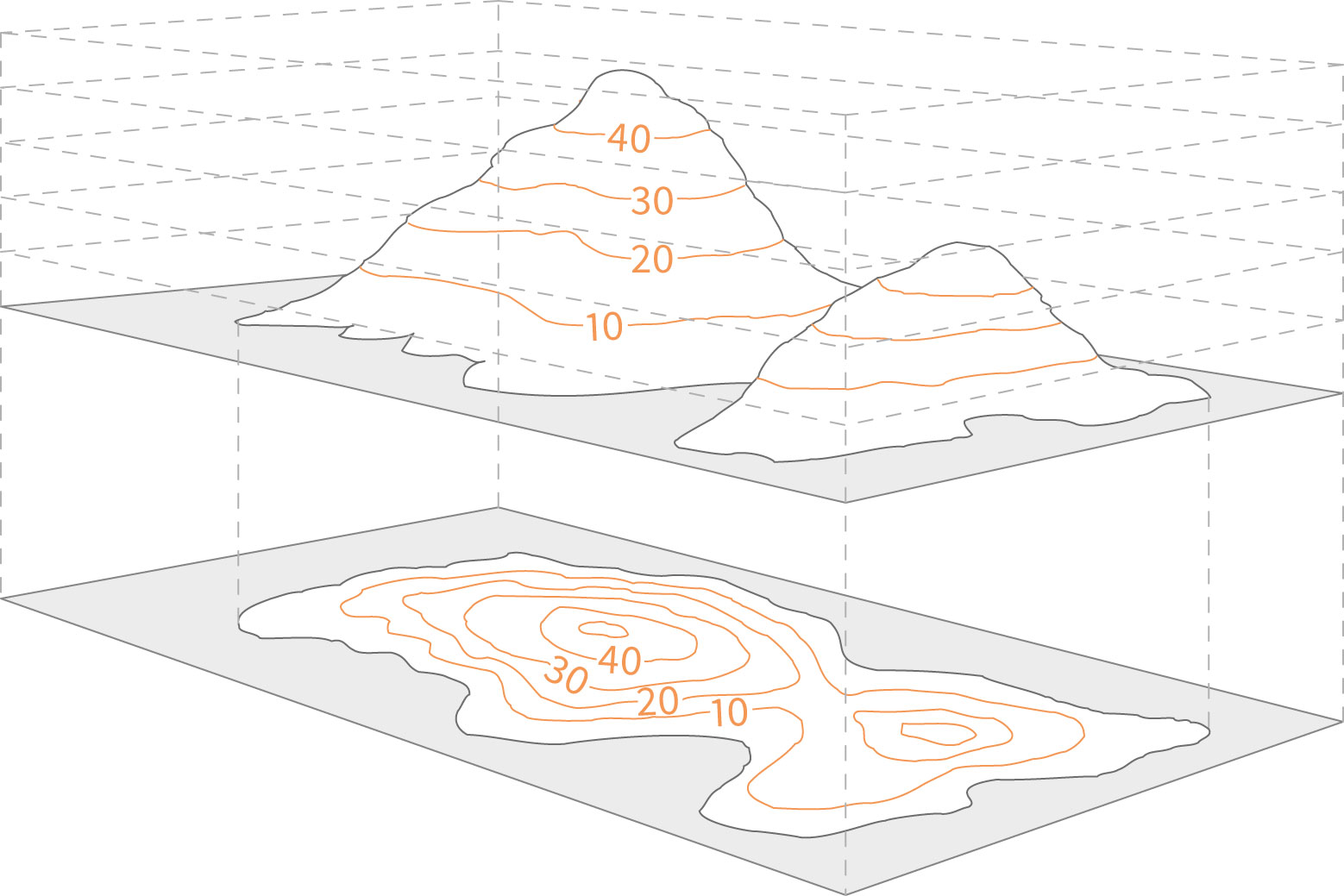
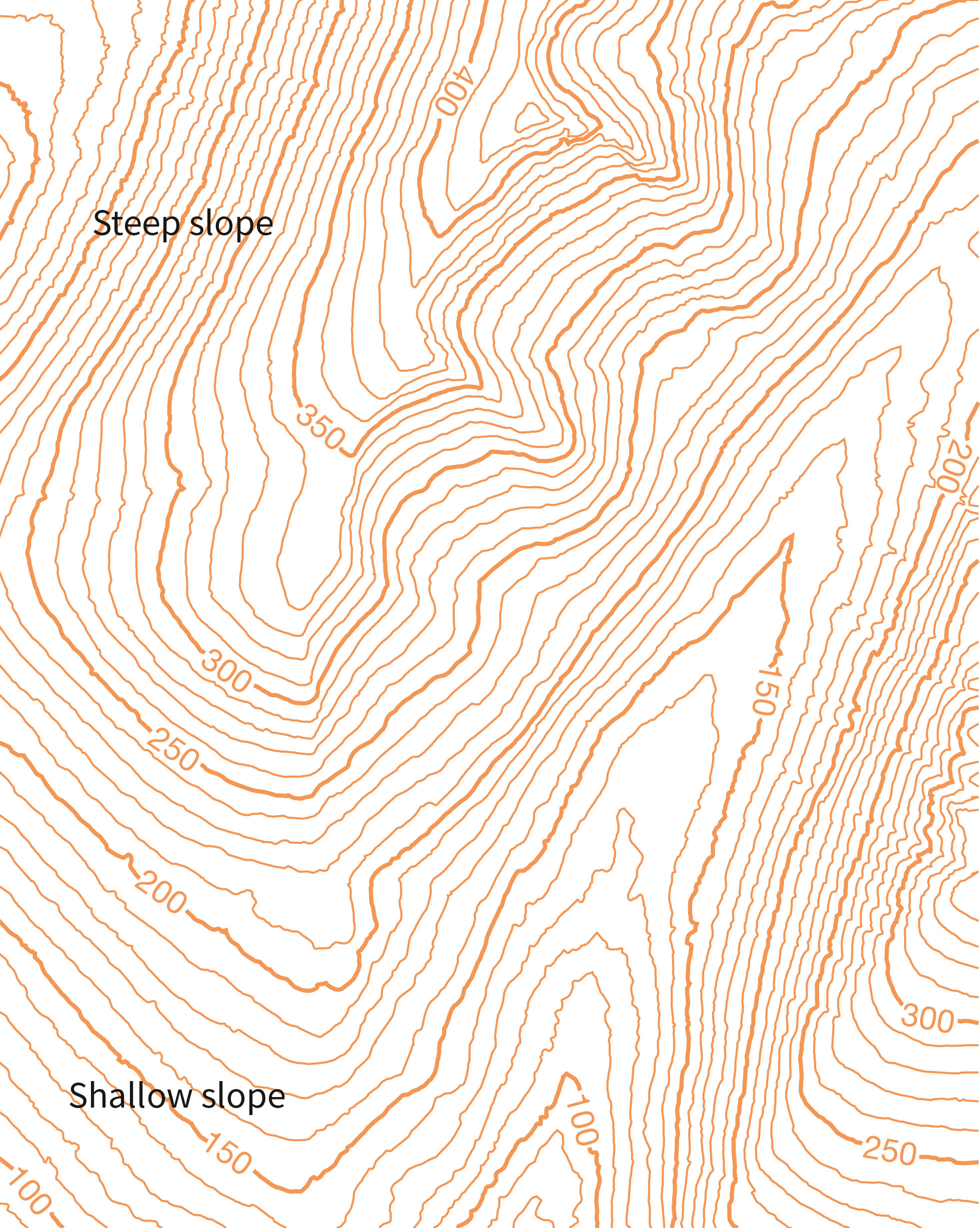
Elevation contours, often referred to as contour lines, are lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation. Imagine slicing through a landscape with a horizontal plane, and then tracing the intersection of that plane with the terrain. This trace, projected onto the map, becomes an elevation contour line.
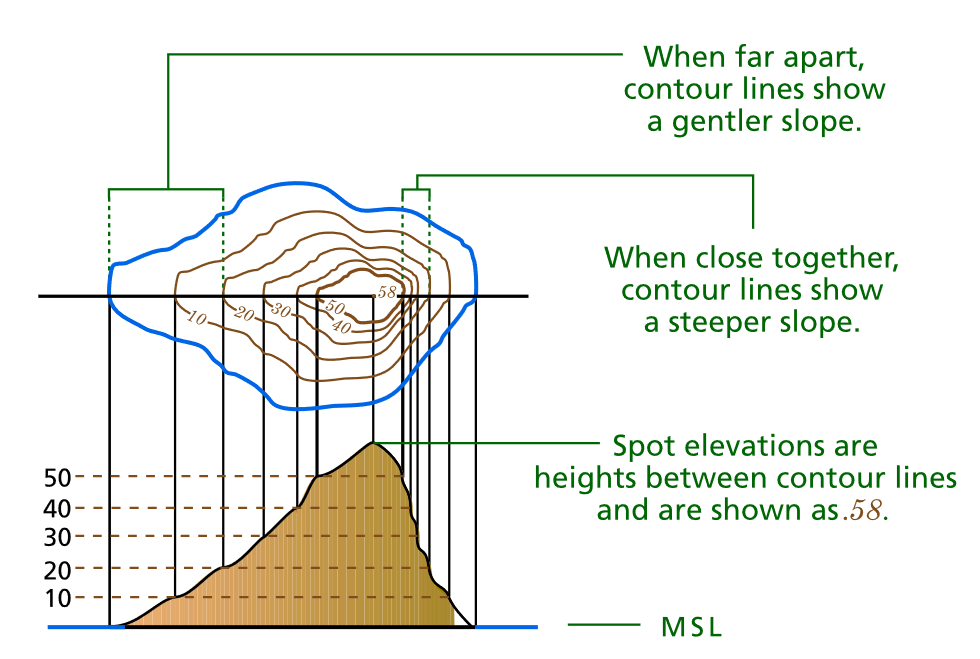
These lines are like invisible slices of the earth, revealing the shape and form of the terrain. The closer the lines are together, the steeper the slope; the further apart they are, the gentler the slope. A single contour line represents a specific elevation, and by reading the scale provided on the map, one can determine the exact elevation of any point along that line.
The Power of Contour Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Maps with elevation contours, often referred to as topographic maps, offer a wealth of information beyond mere elevation. They provide insights into:
-
Landform Recognition: Contours clearly depict the shape of landforms like mountains, valleys, ridges, and depressions. This enables users to visualize the terrain and understand its physical characteristics.
-
Slope Analysis: By observing the spacing of contours, users can assess the steepness of slopes, crucial information for planning hiking trails, determining potential hazards, or evaluating the feasibility of construction projects.
-
Drainage Patterns: Contour maps reveal drainage patterns, as water flows perpendicular to the contours. This helps identify streams, rivers, and potential flood zones, providing vital information for resource management and disaster preparedness.
-
Route Planning: Contours are invaluable for planning routes, especially for activities like hiking, biking, or driving off-road. By understanding the terrain, users can choose paths that are safe, manageable, and offer optimal views.
-
Resource Exploration: Contour maps assist in identifying areas with specific elevation ranges, crucial for exploring resources like water sources, mineral deposits, or suitable land for agriculture.
Beyond Visual Representation: The Importance of Contour Maps
The value of contour maps extends beyond their visual representation. They serve as essential tools in various fields, including:
-
Geography and Geology: Contour maps are fundamental for studying landforms, geological formations, and understanding the processes that shape the Earth’s surface.
-
Civil Engineering and Construction: Engineers use contour maps to plan infrastructure projects, ensuring stability, accessibility, and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Environmental Management: Contour maps help assess the impact of development projects on natural resources and inform sustainable land-use practices.
-
Military Operations: Contour maps are critical for planning military operations, understanding terrain features, and determining optimal routes and positions.
-
Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on contour maps for navigating challenging terrain, planning routes, and assessing potential hazards.
Understanding Contour Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively interpret contour maps, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Contour Interval: This value, usually indicated on the map, represents the elevation difference between each contour line. A contour interval of 20 meters means each line represents a 20-meter increase in elevation.
-
Locate the Index Contours: These are thicker, darker lines with their elevation value labeled. They serve as reference points for identifying the elevation of other contours.
-
Analyze Contour Spacing: The closer the contours are, the steeper the slope. The further apart they are, the gentler the slope.
-
Identify Landforms: Observe the patterns of contours to recognize landforms like hills, valleys, ridges, and depressions.
-
Interpret Drainage Patterns: Water flows perpendicular to contours. Identify streams, rivers, and potential flood zones by tracing the direction of water flow.
Frequently Asked Questions: Deciphering the Language of Contours
Q: What are the different types of contour lines?
A:
- Index Contours: These are thicker, darker lines with their elevation value labeled. They serve as reference points for identifying the elevation of other contours.
- Intermediate Contours: These are thinner lines that lie between index contours.
- Supplementary Contours: These are even thinner lines that represent elevations between intermediate contours, providing finer detail in areas with steeper slopes.
Q: How can I determine the elevation of a specific point on a contour map?
A: If the point lies directly on a contour line, its elevation is the same as that line. If the point lies between contours, estimate its elevation based on its position relative to the surrounding lines and the contour interval.
Q: What are some common features found on contour maps?
A: Contour maps often include additional features like:
- Spot Elevations: These are points with their exact elevation marked on the map.
- Stream Lines: These lines represent the flow of water, indicating drainage patterns.
- Cultural Features: These include roads, buildings, bridges, and other human-made structures.
- Vegetation Symbols: These indicate different types of vegetation, providing information about the environment.
Q: Are contour maps always accurate?
A: Contour maps are created based on surveyed data, but they are subject to some level of error. The accuracy of the map depends on the scale, the quality of the data, and the methods used in its creation.
Q: What are some tips for using contour maps effectively?
A:
- Study the Map Legend: Understand the symbols and conventions used on the map to interpret its features.
- Use a Ruler and Compass: These tools aid in measuring distances, directions, and determining elevations.
- Pay Attention to Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and accuracy.
- Practice: Familiarize yourself with contour maps by studying them and practicing interpreting different features.
Q: What are some resources for learning more about contour maps?
A:
- Online Tutorials: Numerous websites and online courses offer detailed instructions on reading and interpreting contour maps.
- Books and Guides: Several books and field guides provide comprehensive information on topographic maps and their applications.
- Local Hiking Clubs and Organizations: These groups often offer workshops and training sessions on map reading and navigation.
Conclusion: The Language of Landscape
Maps with elevation contours offer a powerful tool for understanding the three-dimensional nature of the earth’s surface. By deciphering the language of contours, users can gain valuable insights into terrain features, slopes, drainage patterns, and other critical information relevant to a wide range of activities. From planning hiking routes to managing natural resources, contour maps play a vital role in navigating the world and understanding the complexities of our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Maps with Elevation Contours. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!