Unveiling the Secrets Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Missouri Soil Temperature Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Missouri Soil Temperature Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Missouri Soil Temperature Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Missouri Soil Temperature Maps
Missouri, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and agricultural bounty, harbors a hidden world beneath its surface. This subterranean realm, governed by the intricate interplay of geological formations, climate, and human activity, is revealed in the form of soil temperature maps. These maps, often overlooked but crucial to understanding the state’s ecological and agricultural dynamics, provide invaluable insights into the thermal conditions influencing plant growth, soil health, and even the distribution of various species.
Understanding the Significance of Soil Temperature
Soil temperature, a fundamental factor shaping the biological processes occurring within the earth’s crust, plays a pivotal role in Missouri’s diverse ecosystems. It influences:
- Plant Growth: Soil temperature directly affects seed germination, root development, and the rate of photosynthesis. Different plant species have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth, making soil temperature maps essential for agricultural planning and crop selection.
- Decomposition: The breakdown of organic matter, a critical process for nutrient cycling and soil fertility, is heavily influenced by soil temperature. Warmer temperatures accelerate decomposition, while colder temperatures slow it down.
- Soil Microorganisms: Soil temperature profoundly impacts the activity and distribution of microorganisms, which play a vital role in nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and overall soil health.
- Water Availability: Soil temperature affects the rate of evaporation and transpiration, influencing the availability of water for plants and the overall moisture content of the soil.
- Pest and Disease Control: Soil temperature can influence the life cycles and activity of pests and diseases, providing valuable information for disease management strategies and pest control measures.
Deciphering Missouri’s Soil Temperature Maps
Missouri soil temperature maps, typically presented as visual representations of temperature data collected over a specific period, offer a comprehensive understanding of thermal conditions across the state. These maps are generated using various methods, including:
- Direct Measurement: Soil temperature sensors are installed at different depths to collect real-time data, providing accurate readings of soil temperature at specific locations.
- Modeling: Computer models, incorporating factors like climate data, soil properties, and vegetation cover, can predict soil temperature patterns across larger areas.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography can be analyzed to estimate soil temperature, providing a broad overview of thermal conditions across the state.
Interpreting the Data: A Key to Understanding Missouri’s Soil
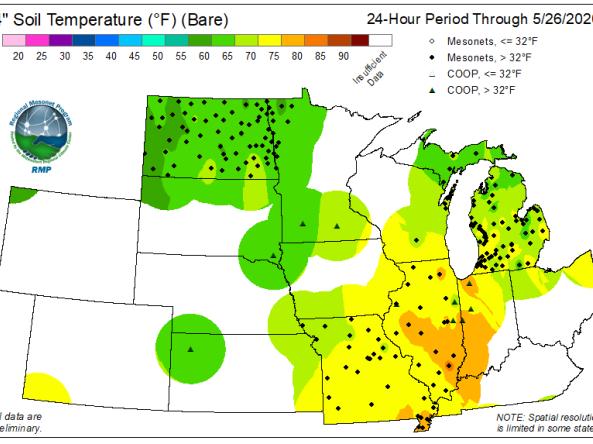
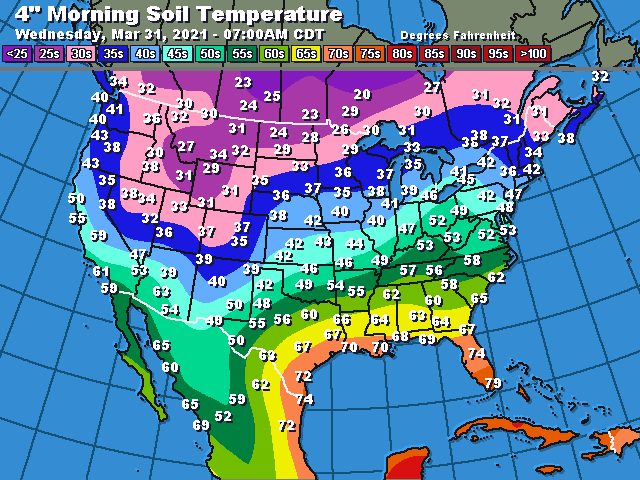
Missouri soil temperature maps are often presented as color-coded representations, where different shades correspond to distinct temperature ranges. These maps can reveal:
- Regional Variations: Missouri’s diverse topography and climate create significant variations in soil temperature across the state. Maps highlight areas with consistently warmer or colder soils, providing insights into regional differences in agricultural suitability and ecological conditions.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Soil temperature fluctuates throughout the year, influenced by factors like air temperature, precipitation, and solar radiation. Maps can depict these fluctuations, highlighting periods of optimal growth for specific crops and the potential for frost damage.
- Depth Profiles: Soil temperature varies with depth, with warmer temperatures typically found near the surface and cooler temperatures deeper down. Maps can illustrate these depth profiles, providing valuable information for understanding root growth and nutrient availability.
- Impact of Human Activities: Land use practices like irrigation, tillage, and the use of fertilizers can significantly alter soil temperature. Maps can reveal the impact of these practices, highlighting areas where human activities have altered the natural thermal regime.
Applications of Missouri Soil Temperature Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Missouri soil temperature maps have a wide range of applications, serving as a vital tool for various stakeholders:
- Agriculture: Farmers can use soil temperature maps to select suitable crops, optimize planting times, and manage irrigation strategies. The maps can also help predict frost risk and identify areas prone to soil compaction, enabling farmers to implement appropriate measures for soil health management.
- Environmental Management: Soil temperature maps are crucial for understanding the impact of climate change on soil ecosystems. They can help identify areas vulnerable to soil degradation, inform conservation strategies, and guide efforts to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Urban Planning: Soil temperature maps can be used to design urban landscapes that minimize the heat island effect, reducing energy consumption and improving urban livability.
- Wildlife Management: Soil temperature influences the distribution and behavior of various wildlife species, making maps valuable for understanding habitat suitability and managing wildlife populations.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Soil Temperature Maps
1. How are soil temperature maps created?
Soil temperature maps are typically created using a combination of direct measurements, modeling, and remote sensing techniques. Direct measurements involve installing soil temperature sensors at different depths to collect real-time data. Modeling uses computer programs to predict soil temperature patterns based on factors like climate data, soil properties, and vegetation cover. Remote sensing relies on satellite imagery and aerial photography to estimate soil temperature across larger areas.
2. What factors influence soil temperature?
Soil temperature is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Air temperature: Air temperature directly affects soil temperature, with warmer air generally leading to warmer soils.
- Solar radiation: Sunlight warms the soil surface, contributing to higher soil temperatures.
- Precipitation: Rainfall can cool the soil surface, especially during dry periods.
- Vegetation cover: Plant cover provides shade and reduces evaporation, moderating soil temperature.
- Soil properties: Soil texture, color, and organic matter content influence how quickly soil heats up and cools down.
- Human activities: Land use practices like irrigation, tillage, and the use of fertilizers can alter soil temperature.
3. What are the benefits of using soil temperature maps?
Soil temperature maps provide valuable insights into the thermal conditions influencing plant growth, soil health, and the distribution of various species. They can be used to:
- Optimize agricultural practices: Select suitable crops, manage irrigation, and predict frost risk.
- Monitor soil health: Identify areas prone to soil degradation and implement conservation strategies.
- Plan urban landscapes: Minimize the heat island effect and improve urban livability.
- Manage wildlife populations: Understand habitat suitability and inform wildlife management strategies.
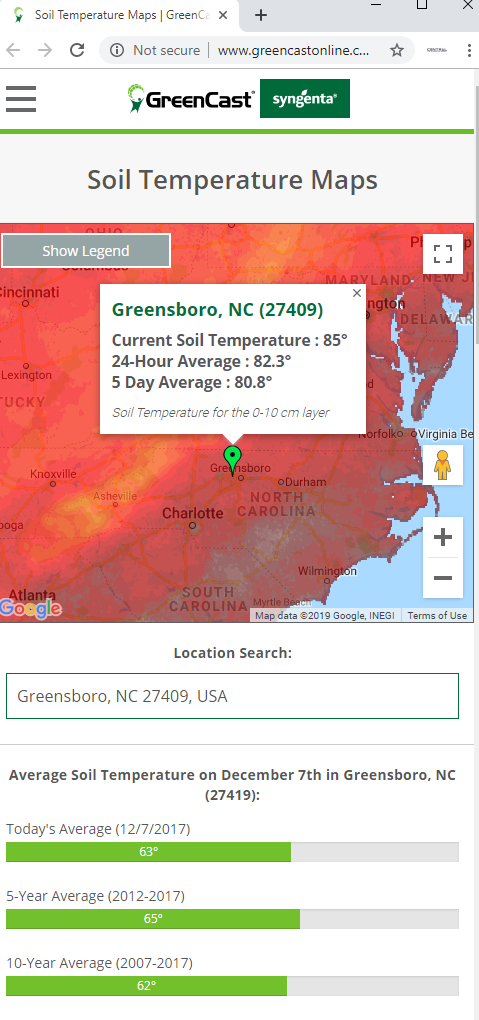
4. How can I access soil temperature maps for Missouri?
Soil temperature maps for Missouri can be accessed through various sources, including:
- Government agencies: The Missouri Department of Agriculture and the University of Missouri Extension provide soil temperature data and resources.
- Research institutions: Universities and research centers often conduct soil temperature studies and make their data publicly available.
- Online databases: Several online databases, such as the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) and the National Soil Survey Center (NSSC), provide soil temperature data and maps.
5. What are some limitations of soil temperature maps?
Soil temperature maps are valuable tools, but they have limitations:
- Spatial resolution: Maps may not capture detailed variations in soil temperature at smaller scales.
- Temporal resolution: Maps typically represent average soil temperatures over a specific period, not real-time fluctuations.
- Data availability: Soil temperature data may not be available for all areas of Missouri.
- Accuracy: Modeling and remote sensing techniques can introduce uncertainties in soil temperature estimates.
Tips for Utilizing Soil Temperature Maps Effectively
- Consider the scale: Soil temperature maps are often presented at different scales. Choose a map with a resolution appropriate for your specific needs.
- Understand the data: Familiarize yourself with the data source, collection methods, and units of measurement used in the map.
- Combine with other data: Integrate soil temperature maps with other data sources, such as soil type maps, climate data, and vegetation maps, for a comprehensive understanding of the soil environment.
- Consult with experts: If you are unsure how to interpret or apply soil temperature maps, consult with experts in soil science, agriculture, or environmental management.
Conclusion: A Window into the Earth’s Hidden World
Missouri soil temperature maps offer a unique and invaluable window into the hidden world beneath the state’s surface. By revealing the thermal dynamics shaping the state’s ecosystems, these maps provide crucial insights for agriculture, environmental management, urban planning, and wildlife conservation. As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change and the need for sustainable practices, the importance of understanding soil temperature and its influence on the environment will only grow. By embracing these maps as a tool for informed decision-making, we can better manage Missouri’s natural resources and ensure a healthy future for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets Beneath the Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Missouri Soil Temperature Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!