Unveiling the Subtropical Realm: A Geographical Journey
Related Articles: Unveiling the Subtropical Realm: A Geographical Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Subtropical Realm: A Geographical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Subtropical Realm: A Geographical Journey

The Earth’s diverse climates are a tapestry woven from temperature, precipitation, and sunlight. Among these, the subtropical regions stand out as zones of transition, bridging the temperate and tropical realms. Characterized by warm temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons, these regions are home to a rich tapestry of ecosystems, diverse cultures, and significant human activity. Understanding the geographical distribution of these subtropical zones is crucial for comprehending their impact on global climate, biodiversity, and human societies.
Defining the Subtropics: A Climate Perspective
The subtropics are not defined by a single, rigid boundary. Instead, they are characterized by a combination of climatic factors:
- Temperature: Subtropical regions experience warm temperatures year-round, with average temperatures ranging from 18°C to 24°C (64°F to 75°F). They are typically located between 23.5° and 40° latitude, both north and south of the equator.
- Precipitation: Subtropical regions exhibit a distinct wet and dry season pattern. The wet season, often associated with monsoons or tropical cyclones, brings significant rainfall. The dry season can be prolonged, leading to drought conditions in some areas.
- Sunlight: Subtropical regions receive ample sunlight throughout the year, contributing to their warm temperatures and supporting lush vegetation.
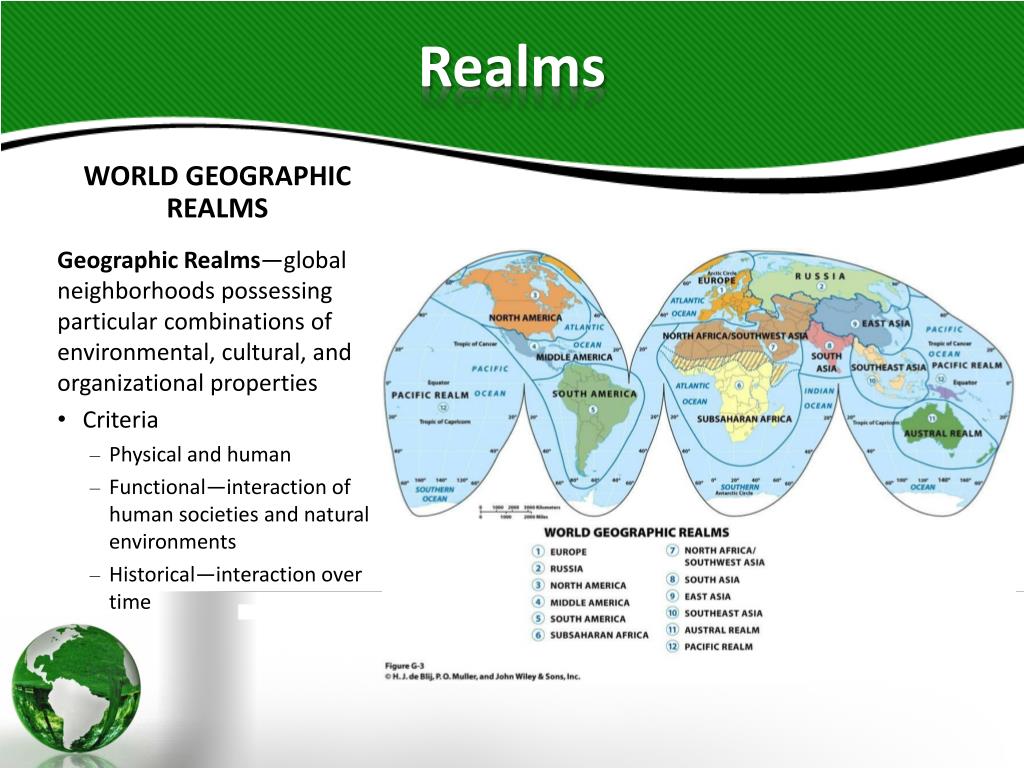
The Subtropical Map: A Visual Representation of Climate Zones
The subtropical map is a visual representation of these climatic characteristics, highlighting the geographical distribution of subtropical regions across the globe. It is a valuable tool for understanding:
- Climate Patterns: The map reveals the distinct wet and dry seasons that define subtropical regions, highlighting the seasonal shifts in precipitation patterns.
- Ecosystem Diversity: Subtropical regions are home to a wide range of ecosystems, including lush forests, savannas, deserts, and coastal areas. The map helps visualize the distribution of these diverse ecosystems.
- Human Activity: Subtropical regions are densely populated and host significant agricultural, industrial, and urban centers. The map provides insights into the distribution of human settlements and economic activities within these zones.
Key Subtropical Regions: A Global Perspective
Subtropical regions are found on all continents, each with its unique characteristics:
- North America: The southeastern United States, Mexico, and parts of Central America fall within the subtropical zone. This region experiences warm, humid summers and mild winters, with significant rainfall during the summer months.
- South America: The eastern coast of South America, including Brazil and Argentina, is characterized by subtropical climates. This region experiences warm temperatures year-round, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Africa: The northern and southern edges of Africa exhibit subtropical climates, with regions like South Africa, Namibia, and parts of North Africa experiencing warm temperatures, dry winters, and wet summers.
- Asia: Eastern China, Japan, and parts of India fall within the subtropical zone. This region experiences hot, humid summers and mild winters, with significant rainfall during the monsoon season.
- Australia: The eastern coast of Australia, including Queensland and New South Wales, is characterized by subtropical climates. This region experiences warm, humid summers and mild winters, with significant rainfall during the summer months.
The Importance of Subtropical Regions: A Global Perspective
Subtropical regions play a crucial role in global climate, biodiversity, and human societies:
- Climate Regulation: Subtropical regions act as a buffer between the tropical and temperate zones, influencing global climate patterns. They contribute to the global circulation of air and water, impacting weather patterns across continents.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Subtropical regions are home to a wide range of plant and animal species, making them biodiversity hotspots. Their diverse ecosystems support a rich tapestry of life, contributing to global biodiversity.
- Agricultural Production: Subtropical regions are major agricultural producers, providing food and resources for global consumption. Their warm temperatures and ample sunlight support the growth of a variety of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Human Settlement: Subtropical regions are densely populated, with major urban centers and industrial hubs. They play a significant role in global trade, commerce, and economic development.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Focus on Sustainability
Subtropical regions also face challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns pose significant risks to subtropical ecosystems and human populations.
- Water Scarcity: Prolonged dry seasons and increasing water demand threaten water resources in many subtropical regions.
- Natural Disasters: Subtropical regions are prone to natural disasters, including hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, posing threats to human life and infrastructure.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and sustainable development:
- Climate Adaptation: Implementing climate adaptation strategies can help mitigate the risks posed by climate change, ensuring the resilience of subtropical ecosystems and human societies.
- Water Management: Sustainable water management practices, such as rainwater harvesting and water conservation, can help address water scarcity and ensure the availability of water resources for future generations.
- Disaster Preparedness: Investing in disaster preparedness measures, including early warning systems and evacuation plans, can help minimize the impact of natural disasters.
FAQs about Subtropical Regions
1. What are the defining characteristics of subtropical climates?
Subtropical climates are characterized by warm temperatures year-round, distinct wet and dry seasons, and ample sunlight. They typically experience average temperatures ranging from 18°C to 24°C (64°F to 75°F).
2. Where are subtropical regions located on the Earth?
Subtropical regions are found between 23.5° and 40° latitude, both north and south of the equator, on all continents.
3. What are some examples of subtropical ecosystems?
Subtropical regions are home to a variety of ecosystems, including lush forests, savannas, deserts, and coastal areas. Examples include the Amazon rainforest, the African savanna, the Sonoran Desert, and the Mediterranean coast.
4. How do subtropical regions contribute to global climate?
Subtropical regions play a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns. They influence the circulation of air and water, impacting weather patterns across continents.
5. What are the major challenges faced by subtropical regions?
Subtropical regions face challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, and natural disasters. These challenges pose threats to ecosystems, human populations, and economic development.
6. What are some opportunities for sustainable development in subtropical regions?
Opportunities for sustainable development in subtropical regions include climate adaptation, water management, and disaster preparedness. These strategies can help mitigate challenges and ensure the long-term resilience of these regions.
Tips for Understanding the Subtropical Map
- Explore the map: Examine the geographical distribution of subtropical regions on the map, paying attention to their location relative to the equator and other climate zones.
- Consider the climate factors: Analyze the temperature, precipitation, and sunlight patterns that define subtropical regions.
- Identify key ecosystems: Identify the different ecosystems found within subtropical regions, such as forests, savannas, deserts, and coastal areas.
- Explore human activity: Consider the distribution of human settlements, agricultural activities, and industrial centers within subtropical regions.
- Connect to global issues: Understand the role of subtropical regions in global climate, biodiversity, and human societies, and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Conclusion: Recognizing the Significance of Subtropical Regions
The subtropical map is a powerful tool for understanding the distribution and significance of these vital regions. By understanding the unique characteristics of subtropical climates, ecosystems, and human activities, we can appreciate their crucial role in global climate, biodiversity, and human societies. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and sustainable development, the subtropical map serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting and managing these vital regions for the benefit of future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Subtropical Realm: A Geographical Journey. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!